Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 21, 2015; 21(27): 8326-8339
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8326
Published online Jul 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8326
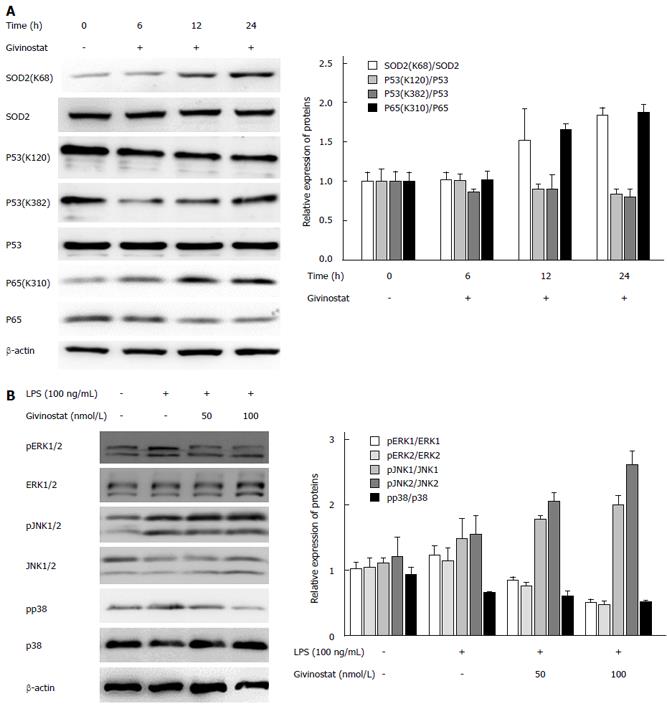
Figure 4 Changes in histone acetylation and regulation of lipopolysaccharide-activated mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling in givinostat-treated JS-1 cells.
A: Effects of givinostat on the post-translational modifications of superoxide dismutase (SOD)2, p53, nuclear factor (NF)-κB, and p65 were analyzed by Western blotting. SOD2 (acetyl K68) acetylation was upregulated, while the expression profile of SOD2 protein showed no significant change. The ratios show a significant difference when compared with those in the control group, in particular at 24 h. Similarly, acetylation of NF-κB p65 (acetyl K310) was upregulated, while its protein expression showed no significant change. There were no obvious changes in the expression profiles of p53, p53 (acetyl K382), and p53 (acetyl K120); B: Expression of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2, phosphorylated ERK1/2, p38, and phosphorylated p38 was upregulated after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment; in contrast, givinostat inhibited the upregulated expression of phosphorylated ERK1/2 and phosphorylated P38 induced by LPS in a time-dependent manner, while no obvious effect on c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)1/2 and phosphorylated JNK1/2 was found.
- Citation: Wang YG, Xu L, Wang T, Wei J, Meng WY, Wang N, Shi M. Givinostat inhibition of hepatic stellate cell proliferation and protein acetylation. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(27): 8326-8339
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i27/8326.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8326