Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2015; 21(26): 8203-8207
Published online Jul 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8203
Published online Jul 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8203
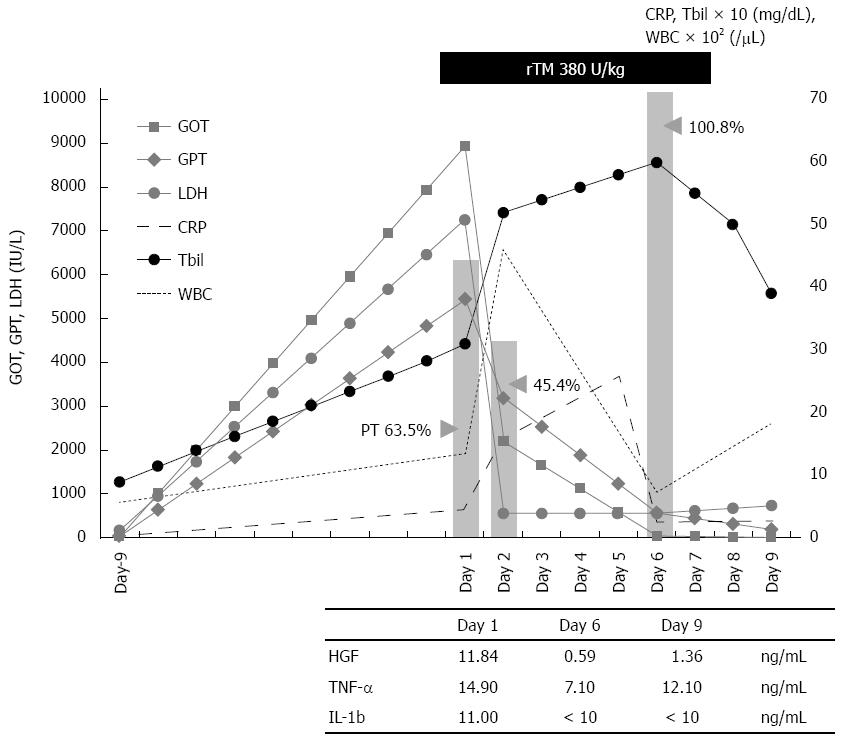
Figure 1 Clinical course of the patient, an 80-year-old Japanese female.
White blood cells (WBC) and C-reactive protein (CRP) recovered within a few days after the initiation of recombinant thrombomodulin (rTM) treatment. PT (indicated by a bar) rose to 100.8% from 54.4%. WBC, CRP, and transaminase (GOT and GPT) all recovered, corresponding to the rTM administration. Tbil: Total bilirubin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; IL: Interleukin.
- Citation: Kurokohchi K, Imataki O, Kubo F. Anti-inflammatory effect of recombinant thrombomodulin for fulminant hepatic failure. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(26): 8203-8207
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i26/8203.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8203