Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2015; 21(26): 8061-8072
Published online Jul 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8061
Published online Jul 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8061
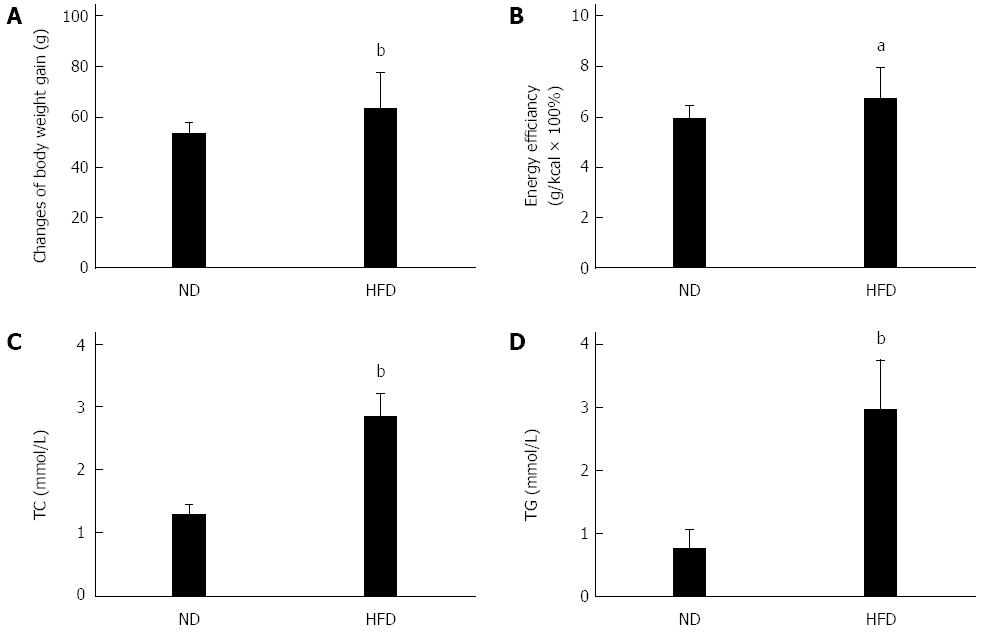
Figure 1 Changes in the basic physiological and biochemical responses of rats fed a high-fat diet.
The normal diet (ND) group (n = 8) was fed a standard diet and the high fat diet (HFD) group (n = 32) was fed a HFD for 10 d. The basic indicators included changes in body weight gain (A), energy efficiency (B), serum total cholesterol (TC) (C), and triglyceride (TG) (D). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs ND group.
- Citation: Qiu X, Gao DH, Xiang X, Xiong YF, Zhu TS, Liu LG, Sun XF, Hao LP. Ameliorative effects of lutein on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(26): 8061-8072
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i26/8061.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i26.8061