Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 7, 2015; 21(25): 7764-7776
Published online Jul 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7764
Published online Jul 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7764
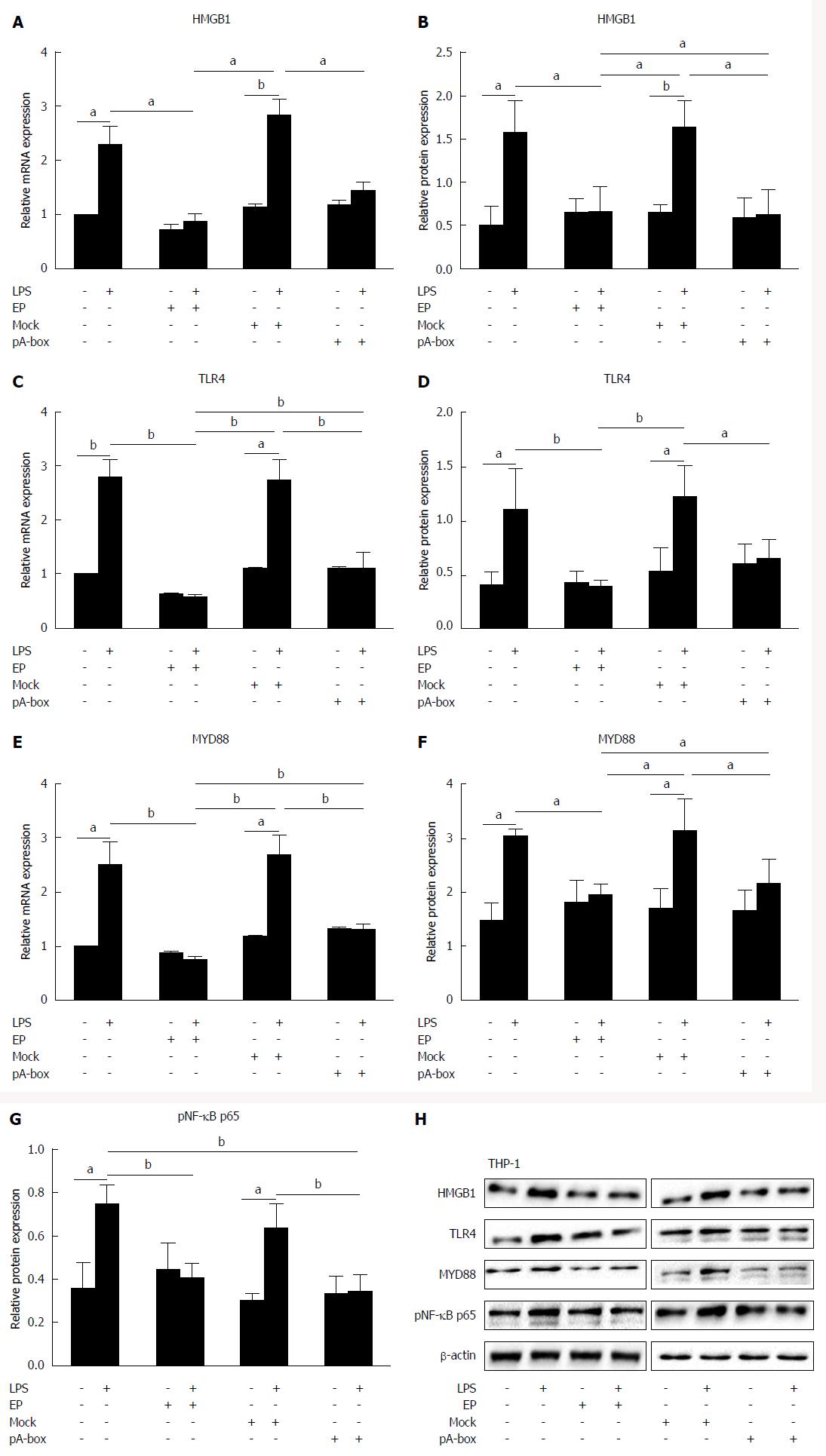
Figure 6 Expression of the HMGB1 protein and TLR4 signaling pathways in THP-1 cells co-cultured with SW480 cells.
After pretreatment with EP (5 mmol/L, 1 h), the SW480 cells were treated with 1 μg/mL LPS and co-cultured with THP-1 cells for 24 h. The HMGB1, TLR4, MYD88, pNF-κB p65 mRNA and protein levels were determined by real-time PCR (A, C, E), densitometric quantification and representative western blots, with β-actin as the loading control (B, D, F, G, H). Compared with the LPS-untreated group, LPS increased HMGB1, TLR4, MYD88, pNF-κB p65 mRNA and protein levels in the THP-1 cells, but EP downregulated these levels. Similarly, HMGB1 A-box also downregulated HMGB1, TLR4, MYD88, pNF-κB p65 mRNA and protein levels compared with the mock-transfected group. The data are expressed as the mean ± SD and are derived from three independent experiments, which were each performed in duplicate. The means with letters above them are significantly different (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control).
-
Citation: Wang FC, Pei JX, Zhu J, Zhou NJ, Liu DS, Xiong HF, Liu XQ, Lin DJ, Xie Y. Overexpression of HMGB1 A-box reduced lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal inflammation
via HMGB1/TLR4 signalingin vitro . World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(25): 7764-7776 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i25/7764.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i25.7764