Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2015; 21(24): 7443-7456
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443
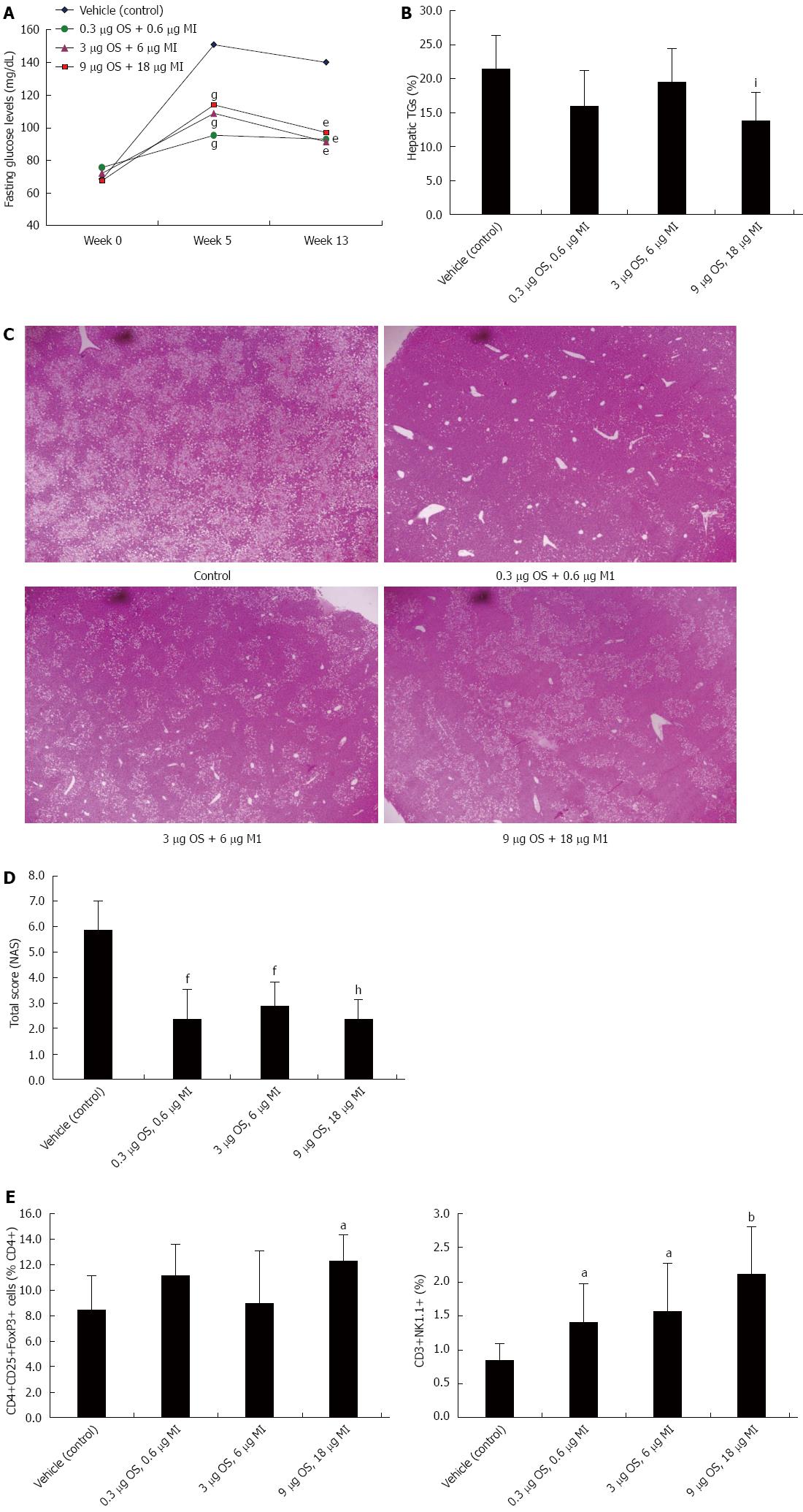
Figure 3 Effect of soy extracts on the high-fat diet/MCD mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
A: The effect of oral administration of soy extracts on fasting serum glucose levels measured on weeks 0, 7 and 13. Glucose levels improved in all treated groups compared to the controls, and the effect was more profound in the 3 μg M1 and 6 μg OS, and 9 μg M1 and 18 μg OS treated groups (eP < 0.01, gP < 0.001 vs control); B: Hepatic triglyceride content was measured in all mice at the end of the study. The combination of 9 μg M1 and 18 μg OS treated groups was associated with significant reduction of hepatic fat content (iP < 0.05 vs control); C: Representative HE (magnification × 10) sections from liver biopsies performed from all groups at the end of the treatment period; D: The pathological NAS score was performed on liver sections from all groups at the end of treatment. A significant improvement was noted in mice in all treated groups (fP < 0.001, hP = 0.0001 vs control); E: FACS analysis was performed on splenocytes for NKT and CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T lymphocytes. Both regulatory lymphocyte subsets significantly increased in the spleen of mice treated with the combination of 9 μg M1 and 18 μg OS (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.005 vs control).
- Citation: Khoury T, Ben Ya'acov A, Shabat Y, Zolotarovya L, Snir R, Ilan Y. Altered distribution of regulatory lymphocytes by oral administration of soy-extracts exerts a hepatoprotective effect alleviating immune mediated liver injury, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and insulin resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(24): 7443-7456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i24/7443.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443