Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2015; 21(24): 7443-7456
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443
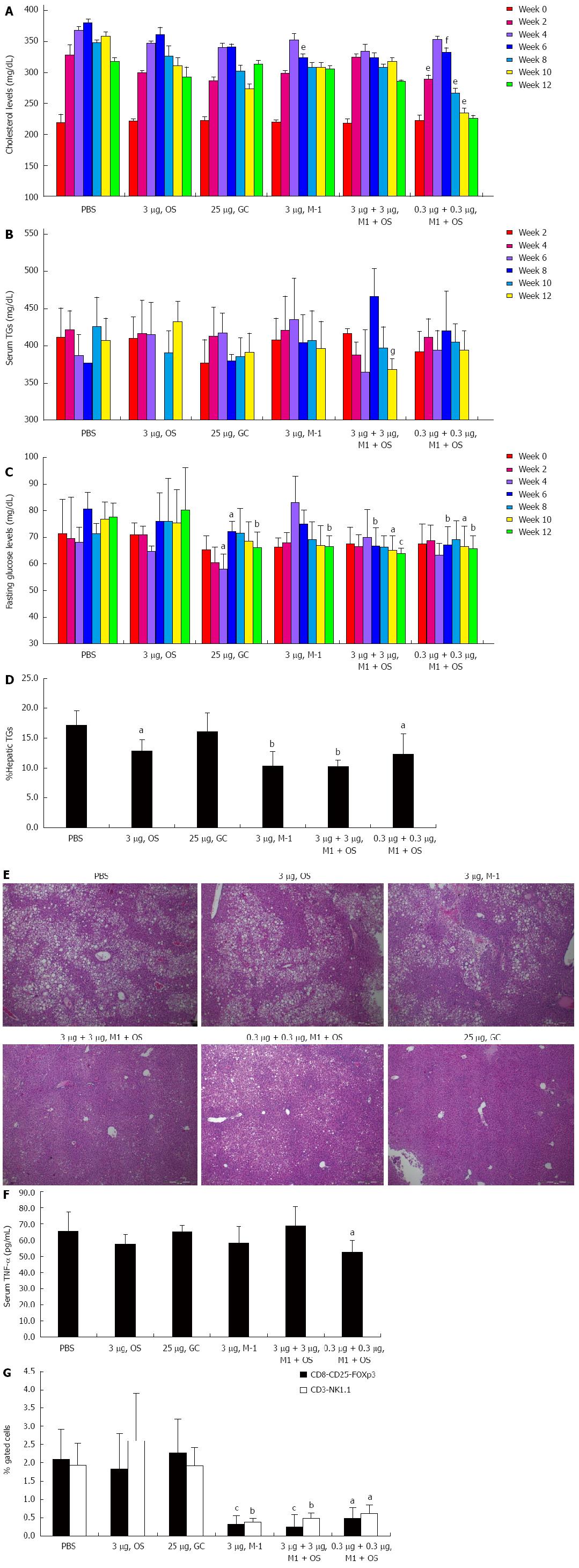
Figure 2 Effect of soy extracts on a high fat diet mouse model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
A: Serum cholesterol levels were measured every two weeks in all groups. The combination of 0.3 μg of OS and M1 was associated with significant a decrease of serum cholesterol level compared to the control group (eP < 0.05, fP < 0.01 vs control); B: Serum triglyceride levels were measured every two weeks in all groups. The combination of 3 μg of each OS and M1 serum levels on week 12 (gP < 0.03 vs control); C: Fasting serum glucose levels were measured every two weeks in all groups. The combination of OS and M1 improved fasting glucose levels as evident from week number 6. A dose of 3 μg of M1 significantly improved fasting glucose level at week 12 (aP < 0.04, bP < 0.008, cP < 0.0005 vs control); D: Hepatic triglyceride content was measured in all mice at the end of the study. The combination of OS and M1, and M1 alone, were associated with significant reduction of hepatic fat content (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.003 vs control); E: Representative H&E (magnification × 10) sections from liver biopsies performed in all groups at the end of the treatment period; F: Serum TNF-α levels were measured by ELISA at the end of the study. A significant reduction was noted in mice treated with the combination of 3 μg M1 and 3 μg OS (aP < 0.05 vs control); G: FACS analysis was performed on splenocytes for NKT and CD8+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T lymphocytes. Both the M1 + OS combination and the M1 alone treated group showed a significant reduction in these subsets (aP < 0.002, bP < 0.0009, cP = 0.0003 vs control).
- Citation: Khoury T, Ben Ya'acov A, Shabat Y, Zolotarovya L, Snir R, Ilan Y. Altered distribution of regulatory lymphocytes by oral administration of soy-extracts exerts a hepatoprotective effect alleviating immune mediated liver injury, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and insulin resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(24): 7443-7456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i24/7443.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443