Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2015; 21(24): 7443-7456
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443
Published online Jun 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443
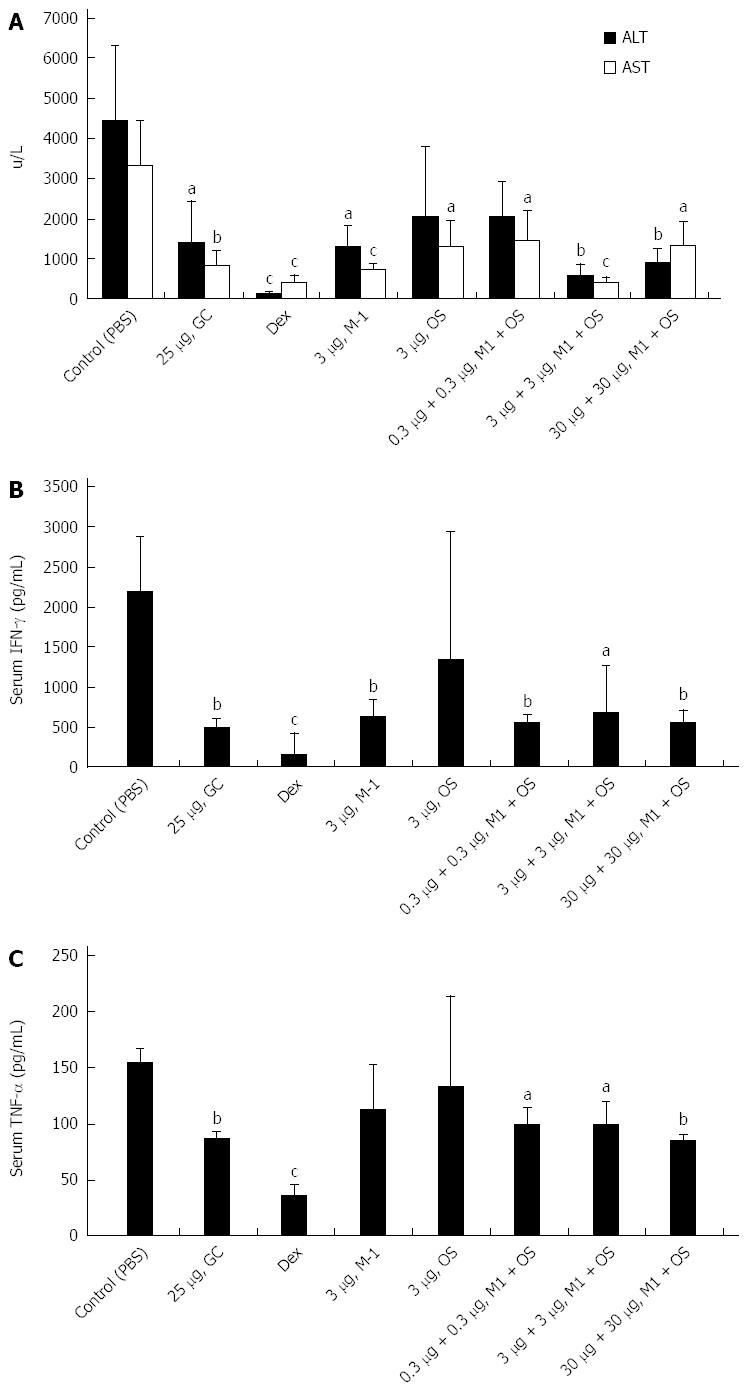
Figure 1 Effect of soy extracts on concanavalin A immune mediated liver injury.
A: Combination of soy extracts in doses of 3 μg and 30 μg of both OS and M1, administered to mice injected with concanavalin A (ConA), significantly decrease aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase serum levels (aP < 0.04, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.004 vs control); B: The combination of OS and M1 soy extracts in all doses and 3 μg M1 were associated with significant reduction of serum interferon gamma levels measured by ELISA at the end of the treatment period (aP < 0.02, bP < 0.005, cP = 0.001 vs control); C: All combinations of soy extracts were associated with a significant decrease in serum TNF-α serum levels measured by ELISA at the end of the study (aP < 0.005, bP = 0.0001, cP = 0.00001 vs control). AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
- Citation: Khoury T, Ben Ya'acov A, Shabat Y, Zolotarovya L, Snir R, Ilan Y. Altered distribution of regulatory lymphocytes by oral administration of soy-extracts exerts a hepatoprotective effect alleviating immune mediated liver injury, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and insulin resistance. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(24): 7443-7456
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i24/7443.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i24.7443