Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2015; 21(23): 7155-7164
Published online Jun 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7155
Published online Jun 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7155
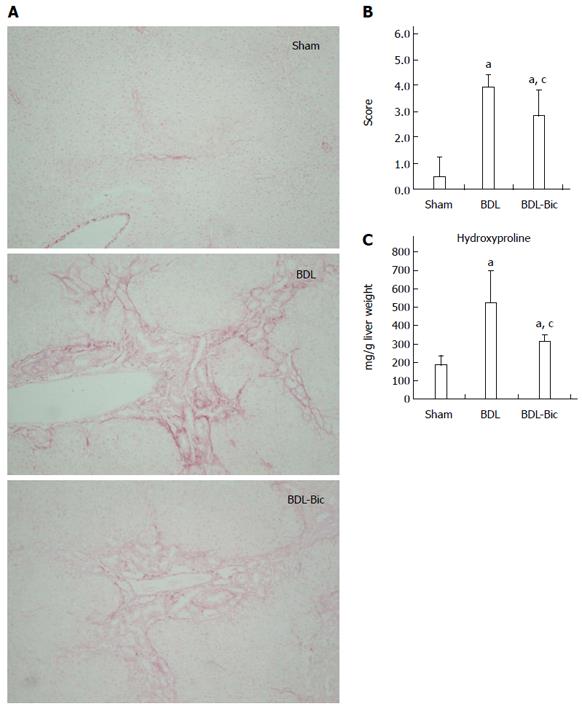
Figure 2 Effects of bicyclol on liver fibrosis of bile duct ligation rats.
Bile duct ligation (BDL) group consisted of animals submitted to undergo BDL operative manipulation and sham-operated animals were used as healthy control. BDL rats were divided into two groups, which orally received sterilized PBS or bicyclol [100 mg/(kg·d)] for consecutive 14 d. Liver sections were stained by Sirius red-stained sections (magnification × 200) (A) and quantified by blinded assessment (B). Hydroxyproline was assayed with frozen liver tissues (C). Data are expressed as mean ± SD of 6 animals per group. aP < 0.05 vs Sham group; cP < 0.05 vs BDL group. Sham: Sham group; BDL: BDL group; BDL-Bic: Bicyclol group.
- Citation: Zhen YZ, Li NR, He HW, Zhao SS, Zhang GL, Hao XF, Shao RG. Protective effect of bicyclol against bile duct ligation-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(23): 7155-7164
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i23/7155.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7155