Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2015; 21(23): 7065-7073
Published online Jun 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7065
Published online Jun 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7065
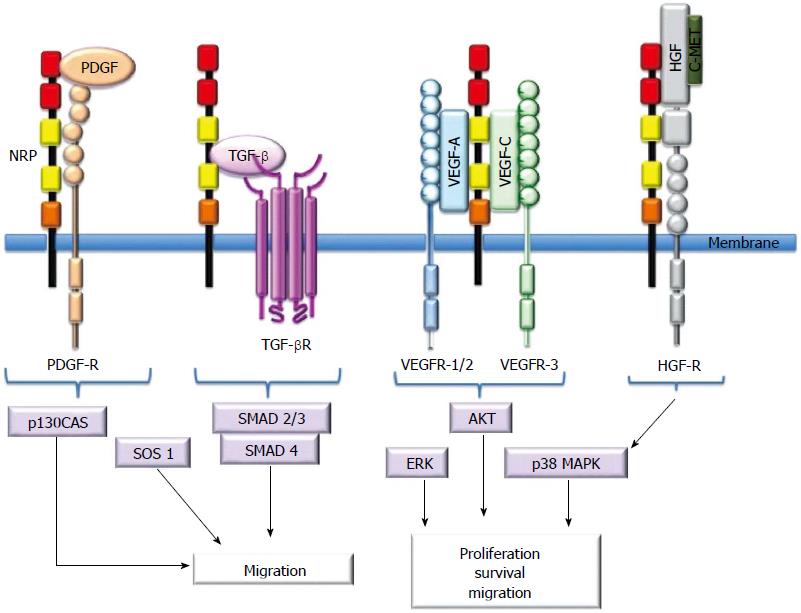
Figure 2 Schematic presentation of neuropilin interactions with ligands and receptors.
Neuropilins (NRPs) bind soluble mediators and their signaling receptors, including the VEGF family, HGF, PDGF, and TGF-β1. NRPs are not absolutely required for receptor signaling, but they enhance the ligand response. NRPs interact with VEGFRs to enhance proliferation, survival and migration. They enhance migration through modulation of PDGF- or TGFβ- and HGF-mediated pathways. NRP: Neuropilin; PDGF: Platelet-derived growth factor; PDGFR: PDGF receptor: TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; TGF-βR: TGF-βR receptor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFR: VEGF receptor; cMet: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; p130Cas: Crk-associated substrat; SOS-1: Son of sevenless guanine nucleotide exchange factor 1; SMAD: Contraction of Sma and Mad (Mothers against decapentaplegic); ERK: Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; p38MAPK: p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.
- Citation: Elpek G&. Neuropilins and liver. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(23): 7065-7073
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i23/7065.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i23.7065