Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2015; 21(22): 6974-6981
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6974
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6974
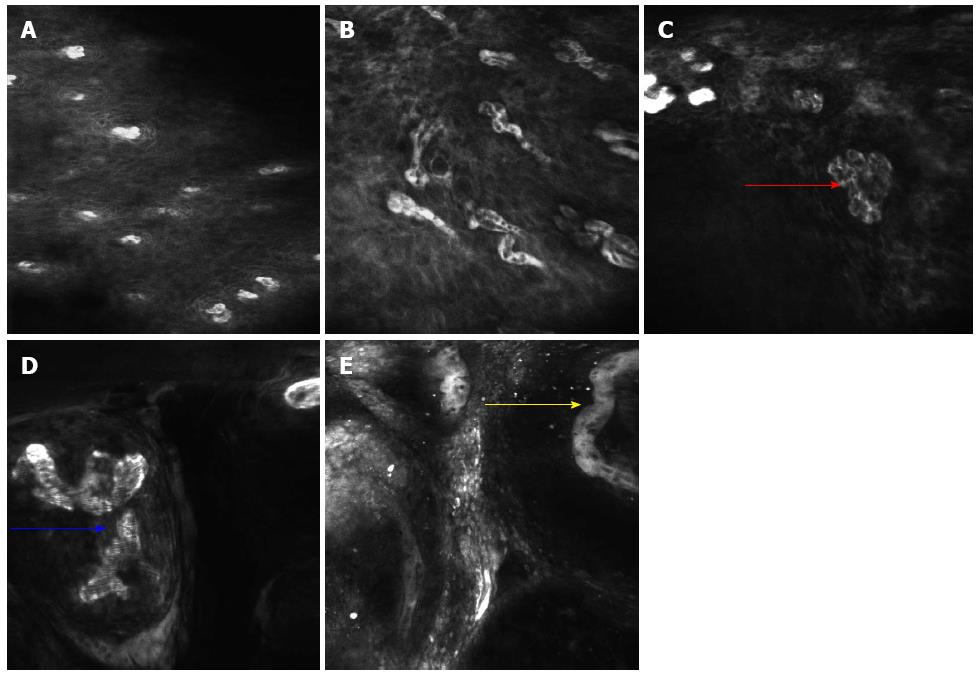
Figure 3 Confocal laser endomicroscopy images showing different intraepithelial papillary capillary loop changes in the esophageal lesions.
A: Regular squamous esophageal epithelium with regular intraepithelial papillary capillary loops (IPCLs) and epithelial cells; B: Some tortuous IPCLs are seen in the non-neoplastic inflammatory lesion; C: Various shapes of twisted IPCLs (red arrow) are seen in the low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia lesion; D: Obvious caliber and shape changes with a larger diameter IPCL (blue arrow) are seen in the high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia lesion; E: Tumor vessels (yellow arrow) are seen in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
- Citation: Huang J, Yang YS, Lu ZS, Wang SF, Yang J, Yuan J. Detection of superficial esophageal squamous cell neoplasia by chromoendoscopy-guided confocal laser endomicroscopy. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(22): 6974-6981
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i22/6974.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6974