Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2015; 21(22): 6872-6883
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6872
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6872
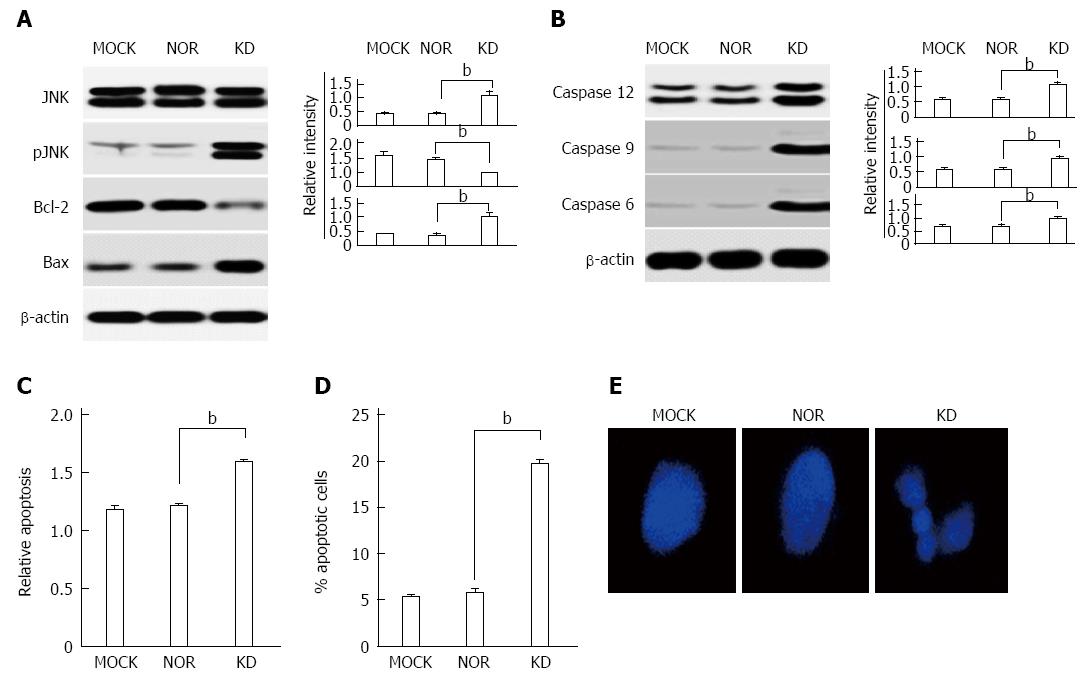
Figure 7 Apoptosis induction by an occult infection related hepatitis B virus S surface antigen variant (KD).
A: After transient transfection of plasmids (MOCK, NOR, and KD) into HuH-7 cells, up-regulation of p-JNK and the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and down-regulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 were observed in the KD HBsAg variant compared to the MOCK and NOR. These results were confirmed using Western blot; B: After transfection, up-regulation of apoptosis-related caspase proteins (caspases 6, 9, and 12) was observed in the KD HBsAg variant compared to the MOCK and NOR. Apoptosis induction in the KD variant was demonstrated using a DNA Fragmentation Assay and the Cell Death Detection ELISAPLUS kit (Roche, Mannheim, Germany); C: PI staining using FACS. Morphological identification (D) of DNA fragmentation (E). The relative intensity values were determined, and all data are expressed as the mean ± SD within a group. The three experiments were compared using Tukey’s multiple post-hoc test (bP < 0.01 vs three experiments).
- Citation: Lee IK, Lee SA, Kim H, Won YS, Kim BJ. Induction of endoplasmic reticulum-derived oxidative stress by an occult infection related S surface antigen variant. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(22): 6872-6883
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i22/6872.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6872