Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 14, 2015; 21(22): 6872-6883
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6872
Published online Jun 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6872
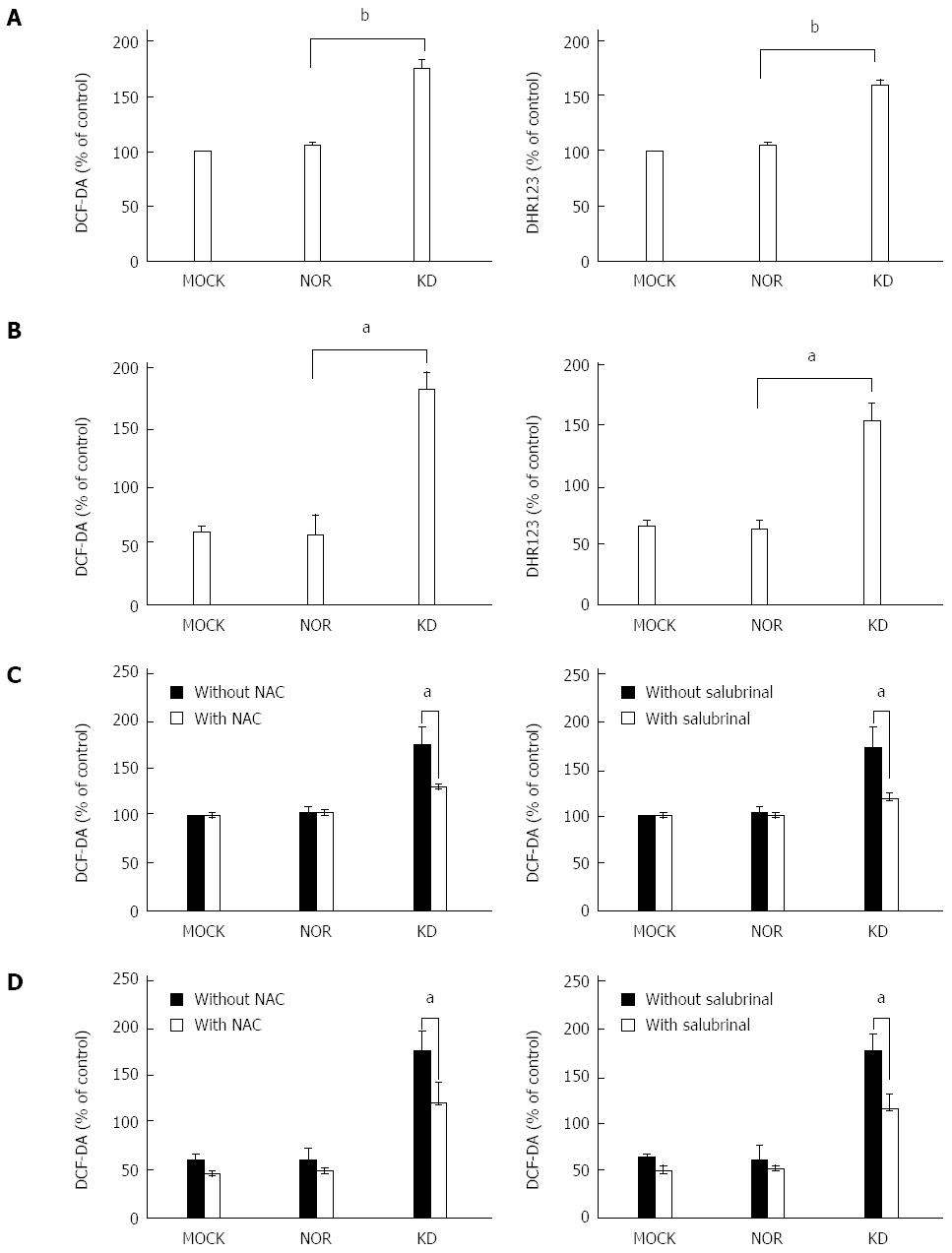
Figure 4 Reactive oxygen species generation by an occult infection related hepatitis B virus S surface antigen variant, KD.
Final concentrations (25 μmol/L) of DCF-DA and DHR123 were incubated for 20 min after transient transfection of plasmids (MOCK, NOR, and KD) into HuH-7 cells to assess mitochondrial and intracellular ROS levels. Results were determined using luminescence spectrometry (A) or FACS (B). The mean values of the experiments are presented in the graphic. The effects of the ROS inhibitor NAC (40 mmol/L) and the ER stress inhibitor salubrinal (70 μmol/L) on ROS generation were evaluated using DCF-DA and luminescence spectrometry (C) or FACS (D). All experiments were performed in triplicate. The relative intensity was determined, and all data are expressed as the means ± SD within a group. Data from the three experiments were compared using Tukey’s multiple post-hoc test (aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control).
- Citation: Lee IK, Lee SA, Kim H, Won YS, Kim BJ. Induction of endoplasmic reticulum-derived oxidative stress by an occult infection related S surface antigen variant. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(22): 6872-6883
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i22/6872.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i22.6872