Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2015; 21(21): 6736-6744
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6736
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6736
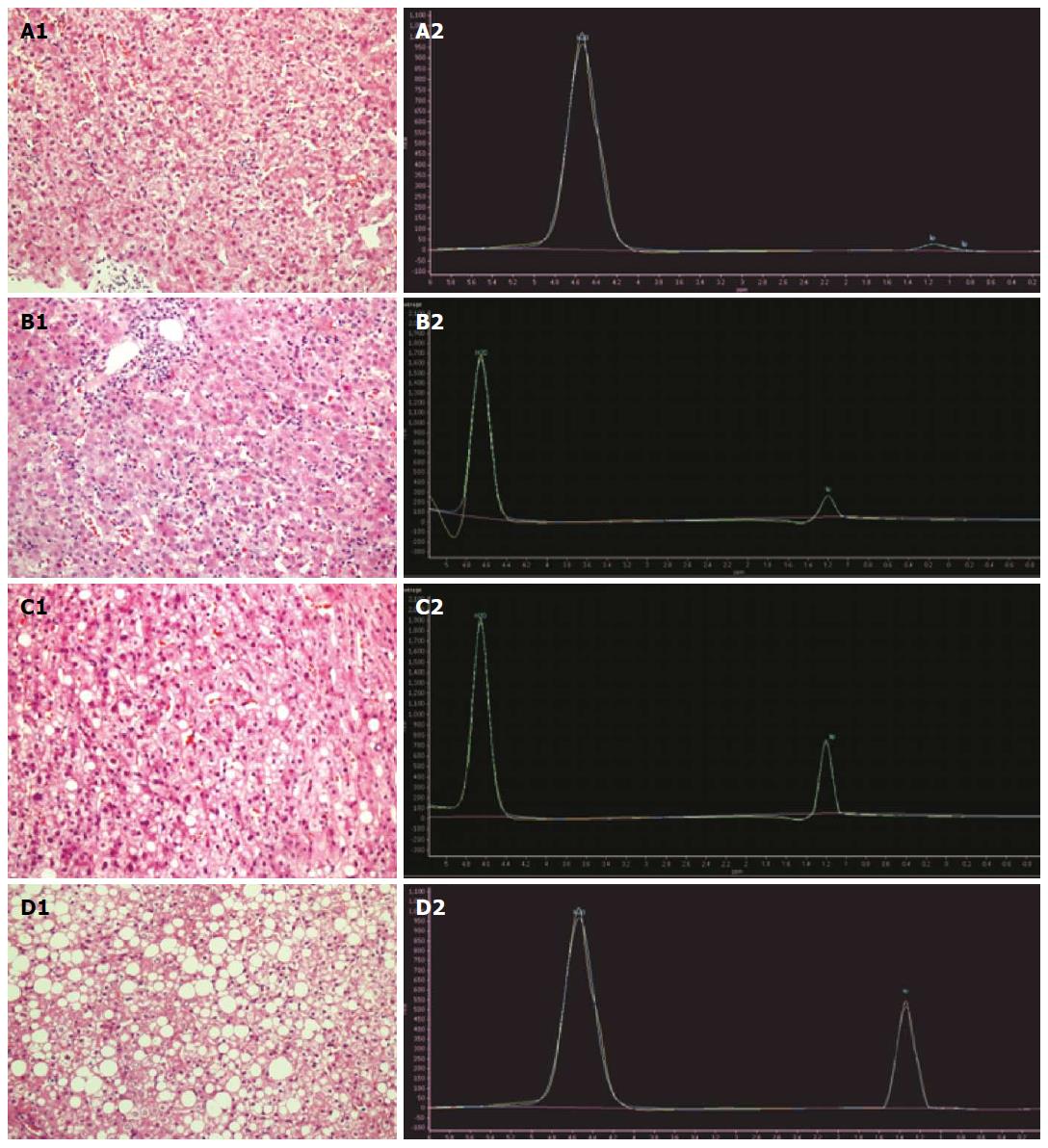
Figure 2 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy spectrum characteristics for different fatty liver pathological levels.
MRS shows short a low fat peak in the no fatty liver group (A1, A2); In mild fatty liver pathological images (B1), lipid droplets increased slightly [hematoxylin-eosin (HE), magnification × 200]; 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) for mild fatty liver showed a slightly increased fat peak (B2); In moderate fatty liver pathological images (C1), lipid drops relatively increased compared with mild fatty liver (HE, magnification × 200); 1H MRS for moderate fatty liver showed a significantly higher fat peak (C2); In severe fatty liver pathological images (D1), the full field distribution of large bubble lipid droplets (HE, magnification × 200); 1H-MRS for severe fatty liver showed a significantly higher fat peak close to the water peak (D2).
- Citation: Zhang Q, Zhang HM, Qi WQ, Zhang YG, Zhao P, Jiao J, Wang JB, Zhang CY. 3.0T 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy for assessment of steatosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(21): 6736-6744
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i21/6736.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6736