Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2015; 21(21): 6582-6590
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6582
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6582
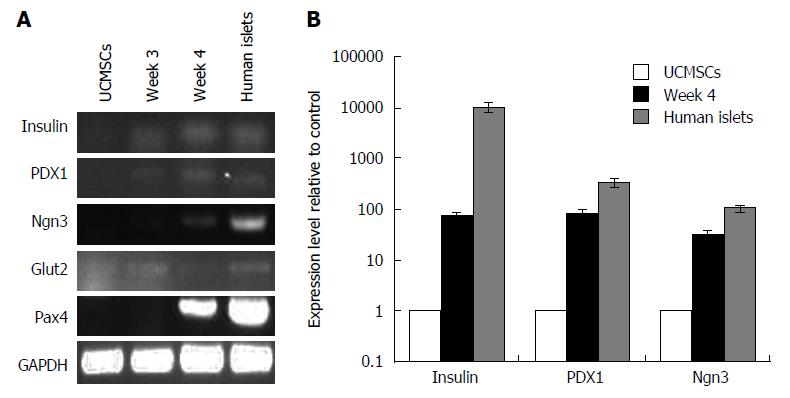
Figure 3 Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analysis of the expression of pancreatic β-cell development-related genes and insulin production-related genes.
A: RT-PCR of the undifferentiated UCMSCs and those during the phases of differentiation (weeks 3 and 4). At the end of differentiation (week 4), the gene expression of IPCs was similar to that of human islets; B: Real-time RT-PCR analysis of UCMSCs. After three-step induction, the UCMSCs expressed high levels of the specific regulation genes for neogenesis and development of pancreatic β-cells, including PDX1, Ngn3 and of hallmark genes for mature islet cells, including insulin. Compared to those of human islets, the differentiated cells (week 4) expressed more Ngn3 and Pax4 and insulin (P < 0.05, n = 3). Each gene was tested in triplicate. RT-PCR: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; UCMSCs: Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells.
- Citation: Yu YB, Bian JM, Gu DH. Transplantation of insulin-producing cells to treat diabetic rats after 90% pancreatectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(21): 6582-6590
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i21/6582.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6582