Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2015; 21(21): 6543-6549
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6543
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6543
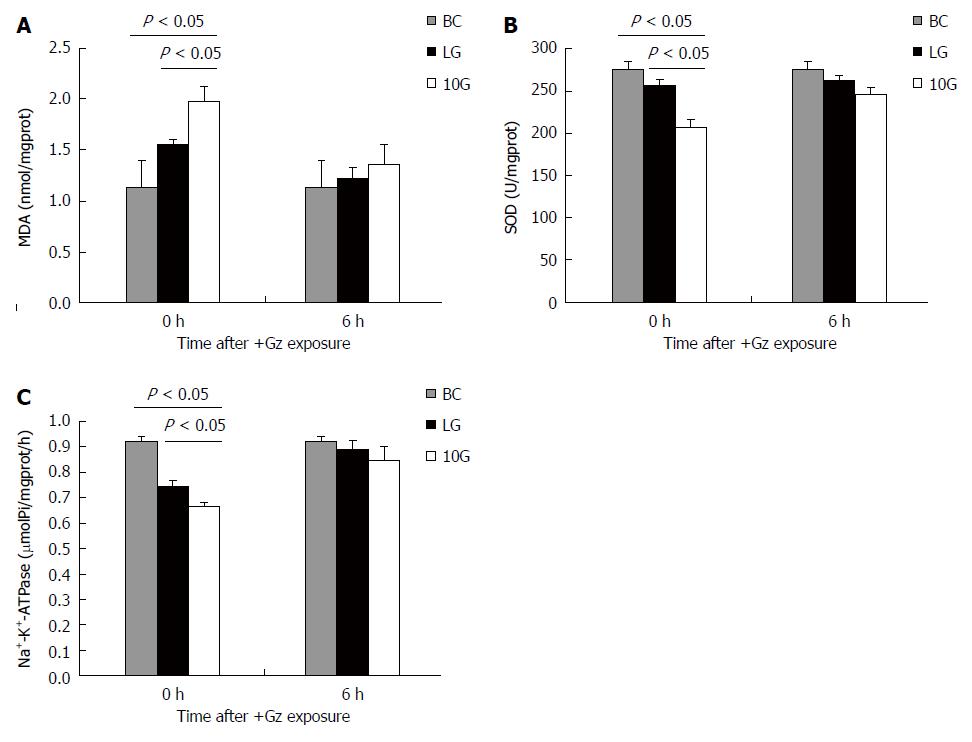
Figure 3 Comparison of the liver tissue malondialdehyde levels (A), the liver tissue superoxide dismutase levels (B) and the rat liver Na+-K+-ATPase activity (C) at 0 and 6 h after +Gz exposures in the blank control group, low G preconditioning group and +10 Gz/5min group.
A: Malondialdehyde (MDA) level in liver tissue of group low G preconditioning (LG) or group +10 Gz/5 min (10G) was higher than that of blank control group at 0 h after exposure (P < 0.05, BC vs 10G). MDA level in liver tissue in LG group was lower than that in 10G group at 0 h after exposure (P < 0.05, LG vs 10G); B: Compared with blank control group, liver tissue superoxide dismutase (SOD) level in LG or 10G group reduced significantly at 0 h after exposure (P < 0.05, vs BC). Compared to 10G group, SOD level was higher in LG group at 0 h after exposure (P < 0.05, LG vs 10G); C: The Na+-K+-ATPase activity in LG group was higher than that in 10G group at 0 h after exposure (P < 0.05, LG vs 10G). BC: Blank control.
- Citation: Shi B, Feng ZQ, Li WB, Zhang HY. Low G preconditioning reduces liver injury induced by high +Gz exposure in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(21): 6543-6549
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i21/6543.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6543