Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2015; 21(21): 6499-6517
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6499
Published online Jun 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6499
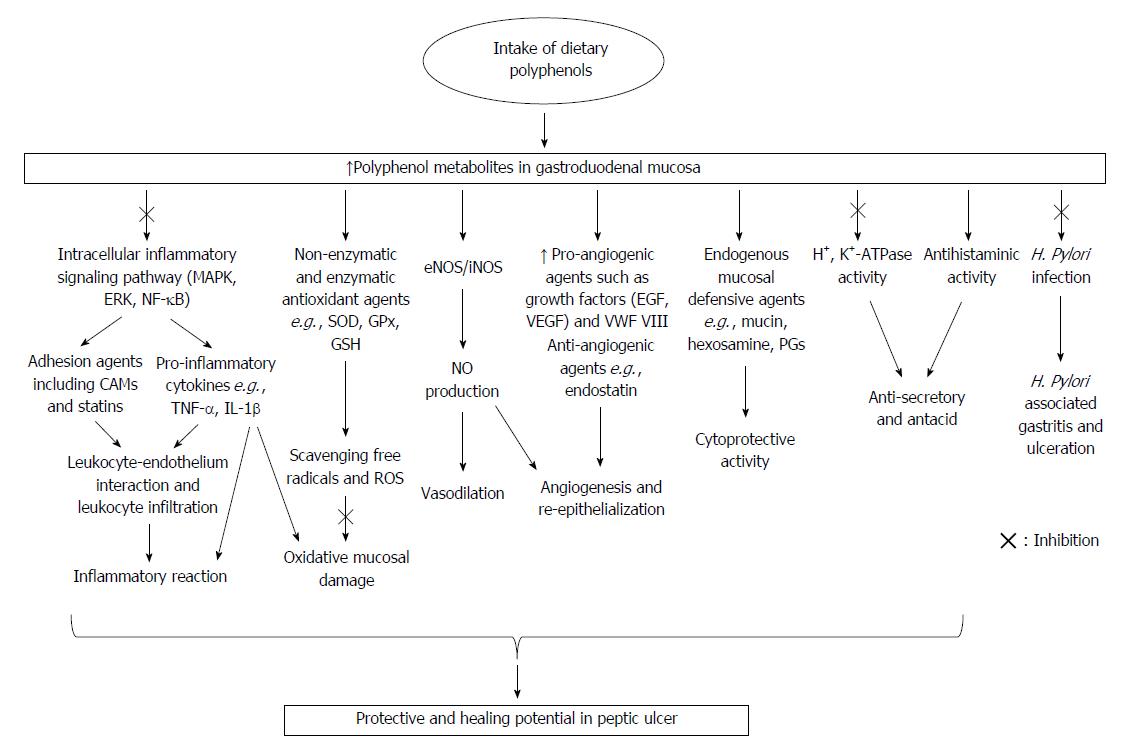
Figure 2 Potential cellular mechanisms of dietary polyphenols as preventive or therapeutic factors in the management of peptic ulcer.
IL: Interleukin; NF: Nuclear factor; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinases; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; GSH: Glutathione; GPx: Glutathione peroxidase; EGF: Epidermal growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; NO: Nitric oxide; vWF: Von Willebrand factor.
- Citation: Farzaei MH, Abdollahi M, Rahimi R. Role of dietary polyphenols in the management of peptic ulcer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(21): 6499-6517
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i21/6499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i21.6499