Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2015; 21(20): 6252-6260
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6252
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6252
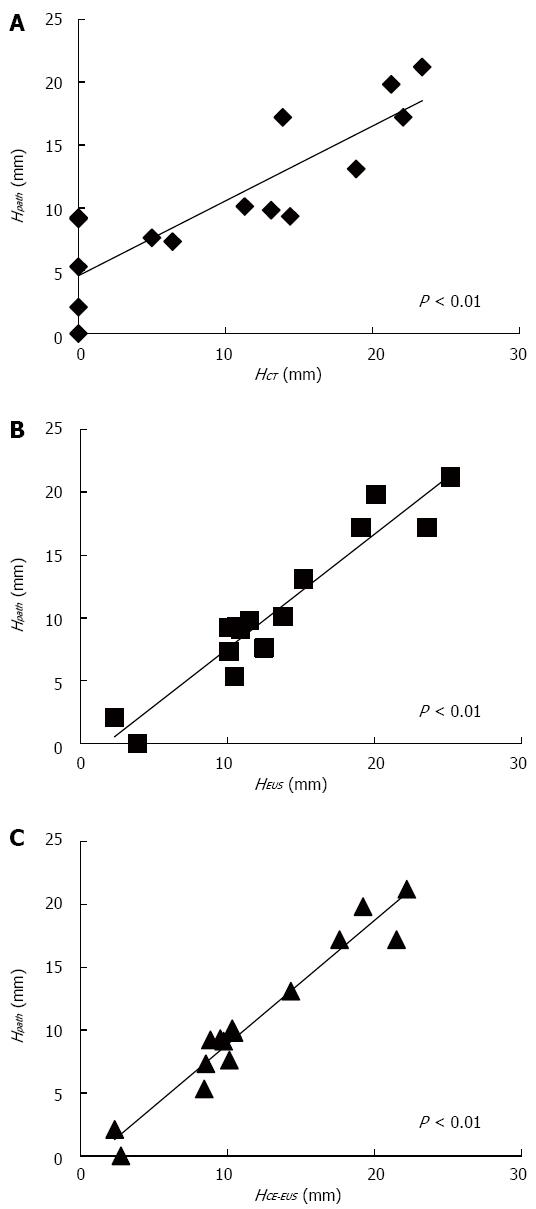
Figure 2 Correlations between mural nodules height measured by each imaging modality and mural nodules height measured on pathological specimens.
A: A positive correlation was identified between MN height measured by CT and that measured on pathological specimens; B: A positive correlation was identified between MN height measured by EUS and that measured on pathological specimens; C: A positive correlation was identified between MN height measured by CE-EUS and that measured on pathological specimens. HCT: MN height measured by CT; HEUS: MN height measured by EUS; HCE-EUS: MN height measured by CE-EUS; HPath: MN height measured on pathological specimens; MN: Mural nodule; CT: Computed tomography; EUS: Endoscopic ultrasonography; CE-EUS: Contrast-enhanced EUS.
- Citation: Harima H, Kaino S, Shinoda S, Kawano M, Suenaga S, Sakaida I. Differential diagnosis of benign and malignant branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm using contrast-enhanced endoscopic ultrasonography. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(20): 6252-6260
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i20/6252.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6252