Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2015; 21(20): 6180-6193
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6180
Published online May 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6180
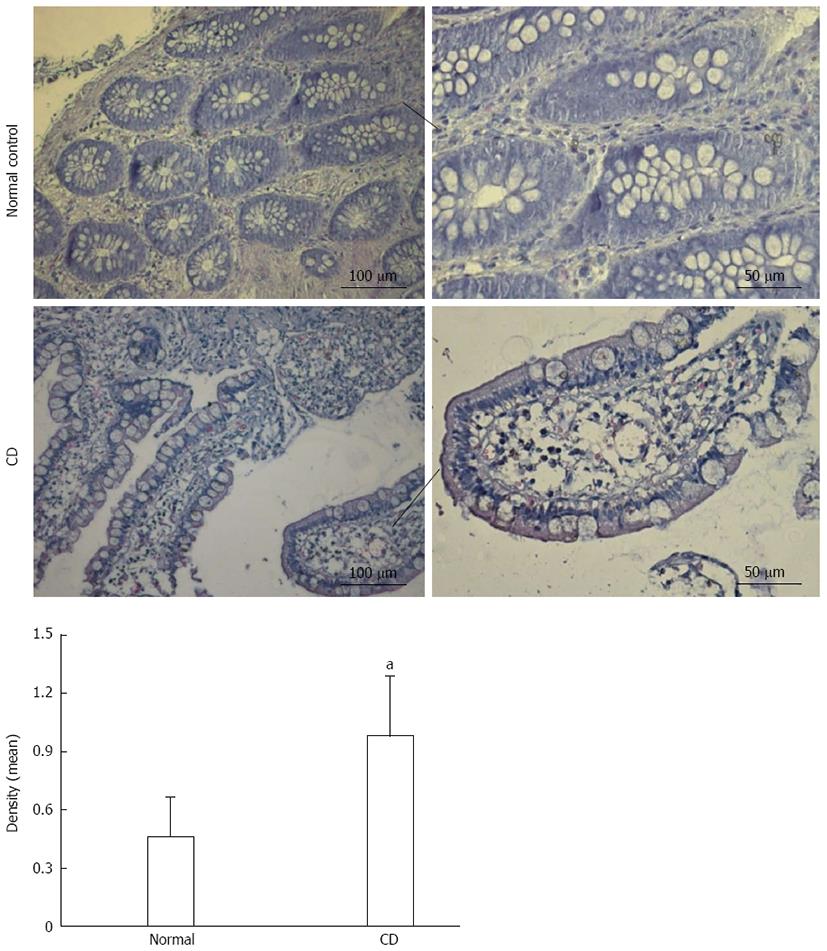
Figure 1 Serum-and-glucocorticoid-inducible-kinase-1 expression was increased in intestinal epithelial cells of patients with Crohn’s disease.
Immunohistochemistry of serum-and-glucocorticoid-inducible-kinase-1 (SGK1) in samples from patients with active Crohn’s disease (CD) and normal controls. Weak staining of SGK1 was detected in the samples from normal controls, while strong staining of SGK1 was observed in samples from patients with active CD. The CD group (n = 8) had 4 males and 4 females. The normal control group (n = 8) had 4 males and 4 females. aP < 0.05 vs normal controls. SGK1: Serum-and-glucocorticoid-inducible-kinase-1.
-
Citation: Bai JA, Xu GF, Yan LJ, Zeng WW, Ji QQ, Wu JD, Tang QY. SGK1 inhibits cellular apoptosis and promotes proliferation
via the MEK/ERK/p53 pathway in colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(20): 6180-6193 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i20/6180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i20.6180