Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 14, 2015; 21(2): 439-452
Published online Jan 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.439
Published online Jan 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.439
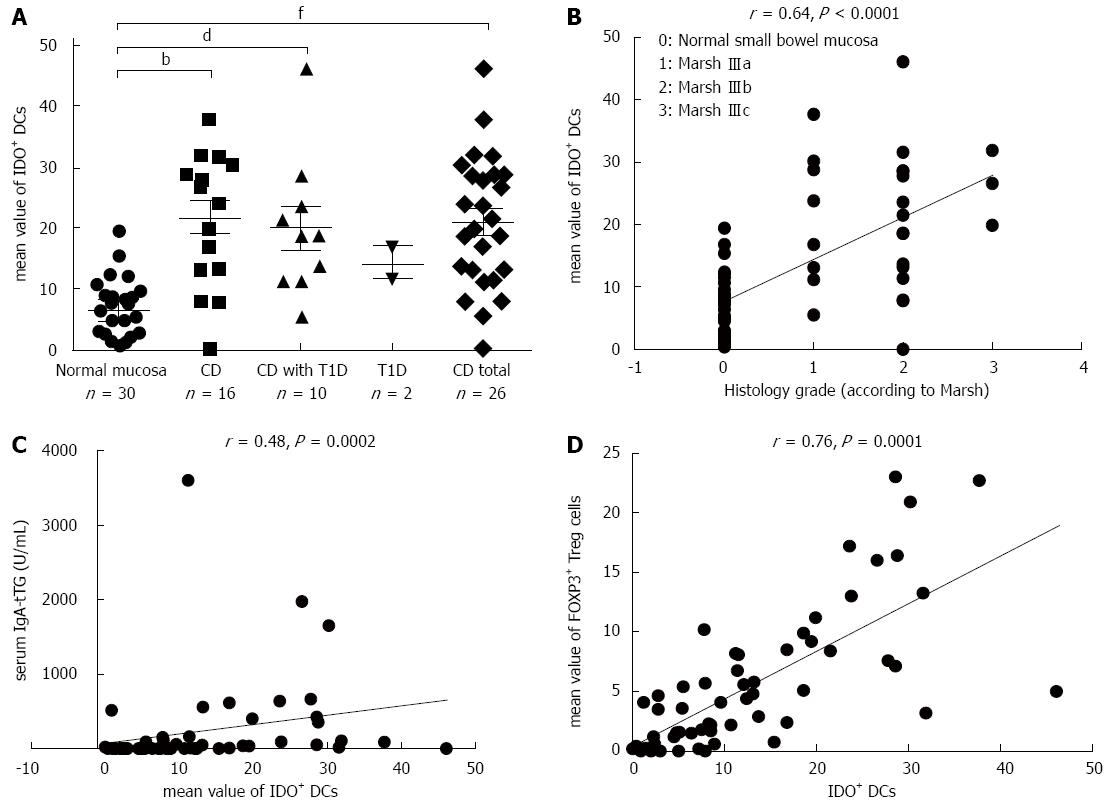
Figure 4 Densities of IDO+ DCs on paraffin sections for the different study groups (A); Spearman’s rank correlation between the histological grades (according to Marsh) and IDO+ DCs (on paraffin sections) for the studied persons (B); between the densities of IDO+ DCs and serum IgA-tTG levels in the studied persons (C); or between the densities of IDO+ DCs and FOXP3+ Treg cells for the entire study group, evaluated on paraffin sections (r = 0.
76; P = 0.0001) (D). The dots represent the mean values of positively stained cells per microscopic field. bP < 0.01, CD vs normal mucosa; dP < 0.01, CD with T1D vs normal mucosa; fP < 0.01, CD total vs normal mucosa. CD: Celiac disease; DC: Dendritic cell; T1D: Type 1 diabetes; IgA-tTG: IgA antibody; Tregs: regulatory T cells; IDO: Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase.
- Citation: Vorobjova T, Uibo O, Heilman K, Uibo R. Increased density of tolerogenic dendritic cells in the small bowel mucosa of celiac patients. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(2): 439-452
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i2/439.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i2.439