Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2015; 21(18): 5473-5481
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5473
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5473
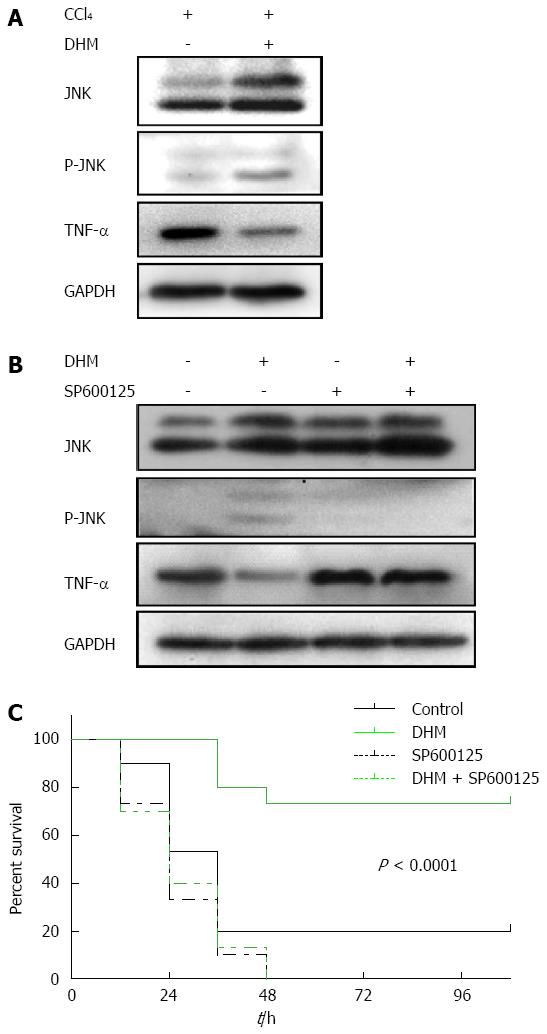
Figure 5 Dihydromyricetin protects from CCl4-induced acute liver failure by up-regulating JNK activation both in liver injury mice and acute liver failure mice.
A: Western blots depicting JNK pathway proteins on day 2 after CCl4 (1 mL/kg) injection; B: Western blots depicting JNK pathway proteins on day 2 after CCl4 (2.6 mL/kg) injection with or without of SP600125 treatment; C: The survival curves of the different conditions (n = 30/group).
-
Citation: Xie J, Liu J, Chen TM, Lan Q, Zhang QY, Liu B, Dai D, Zhang WD, Hu LP, Zhu RZ. Dihydromyricetin alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury
via JNK-dependent mechanism in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(18): 5473-5481 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i18/5473.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5473