Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2015; 21(18): 5473-5481
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5473
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5473
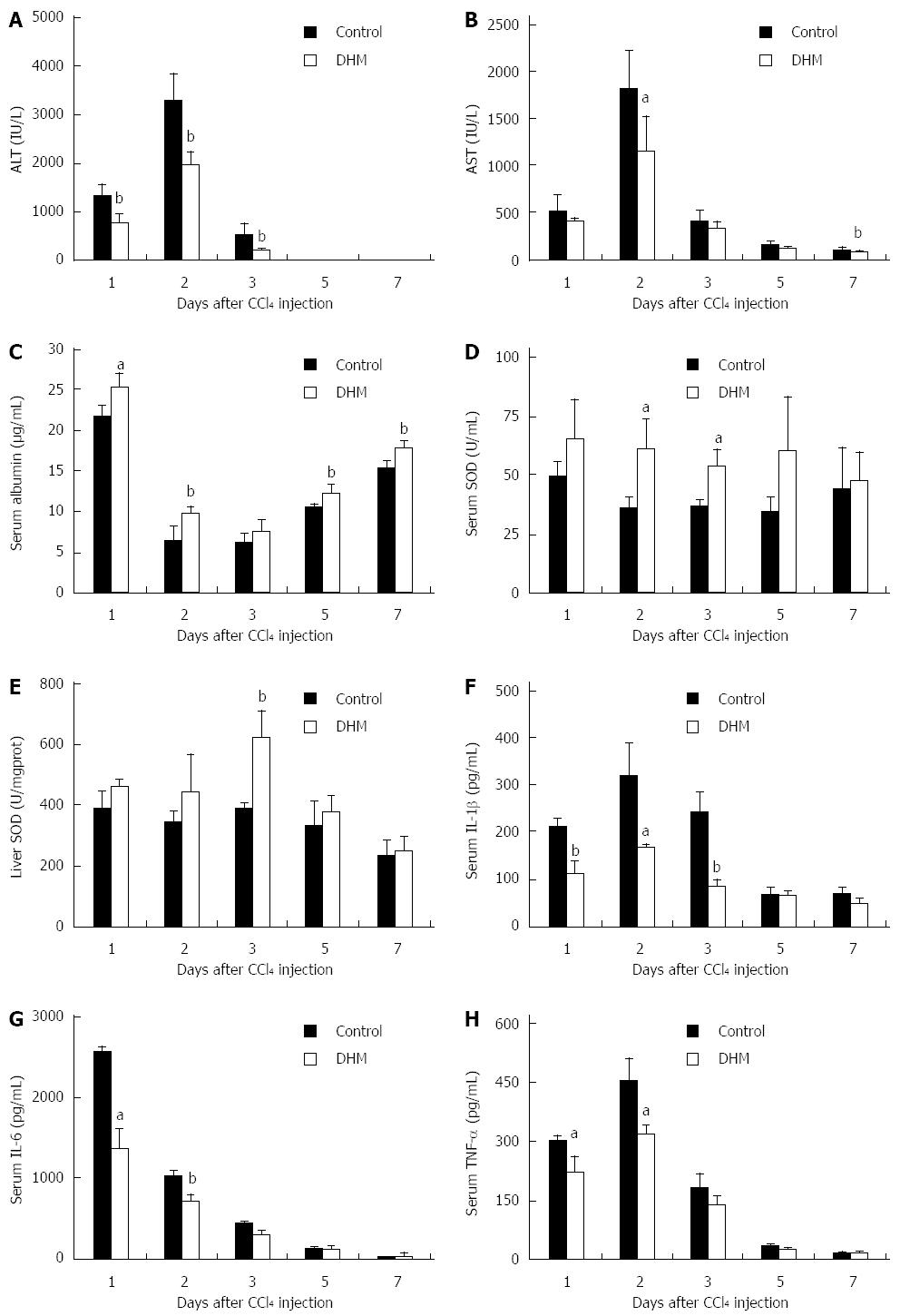
Figure 1 Dihydromyricetin protects mice against CCl4-induced liver injury.
Mice were treated with CCl4 (1 mL/kg body weight and 1:3 diluted in corn oil) to induce acute liver injury, and then orally administered with DHM (80 mg/kg body weight and diluted in CMC-Na) 2 h after CCl4 injection, once per day for 4 d. Control mice were treated with an equal volume of CMC-Na. Subsequently, serum ALT, AST, albumin, SOD, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α and liver SOD were measured at indicated time points and determined as described in materials and methods. A: Serum ALT; B: Serum AST; C: Serum Albumin; D: Serum SOD; E: Liver SOD; F: Serum IL-1β; G: Serum IL-6; H: Serum TNF-α. Values represent mean ± SE (n = 6). aP < 0.05 and bP < 0.01 vs control, respectively.
-
Citation: Xie J, Liu J, Chen TM, Lan Q, Zhang QY, Liu B, Dai D, Zhang WD, Hu LP, Zhu RZ. Dihydromyricetin alleviates carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury
via JNK-dependent mechanism in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(18): 5473-5481 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i18/5473.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5473