Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2015; 21(18): 5465-5472
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465
Published online May 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465
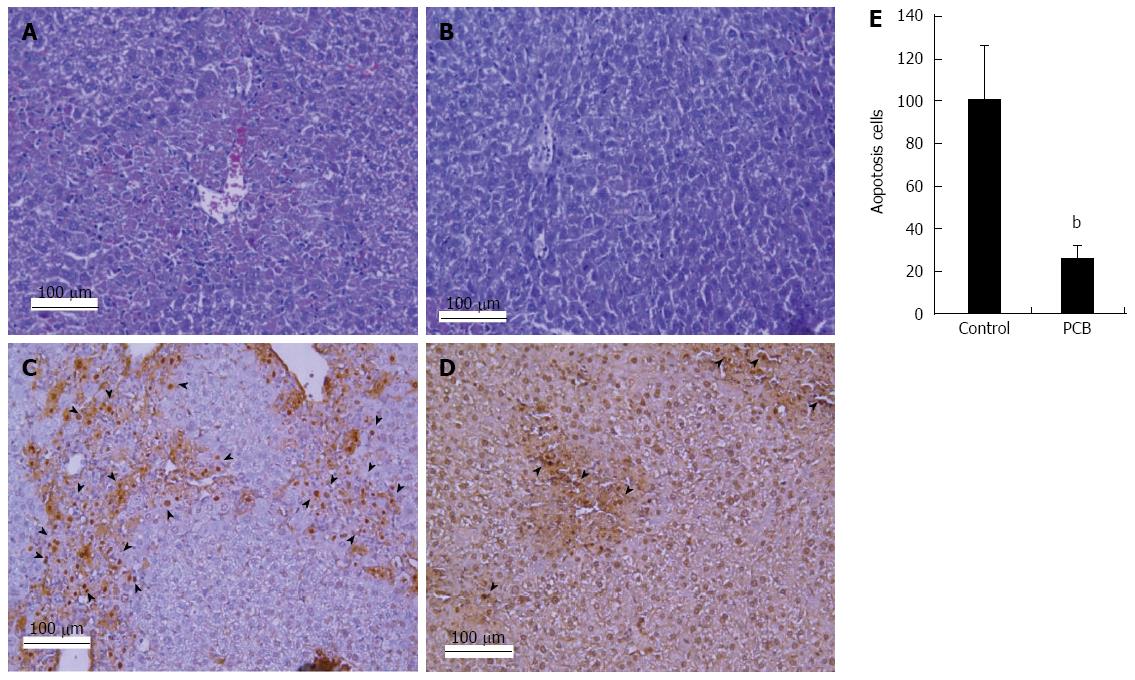
Figure 3 Phycocyanobilin reduces hepatocellular necrosis and apoptosis.
A: Liver section of control group stained with HE at day 2 after CCl4 injection of mice, showing partial necrosis with clusters of inflammatory cells around central vein; B: Liver section of PCB group stained with HE at day 2 after CCl4 injection of mice, demonstrating decreased inflammatory cells and histological recovery compared with control group. In the TUNEL assay earthy yellow cells indicate apoptotic cells; C: The control group; D: PCB treated group; E: Demonstrated numbers of apoptotic cells. At least six 12 mm2 tissue sections were counted for each group. Values represent mean ± SE (n = 6), bP < 0.01 vs control.
- Citation: Liu J, Zhang QY, Yu LM, Liu B, Li MY, Zhu RZ. Phycocyanobilin accelerates liver regeneration and reduces mortality rate in carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury mice. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(18): 5465-5472
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i18/5465.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i18.5465