Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2015; 21(16): 5009-5016
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.5009
Published online Apr 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.5009
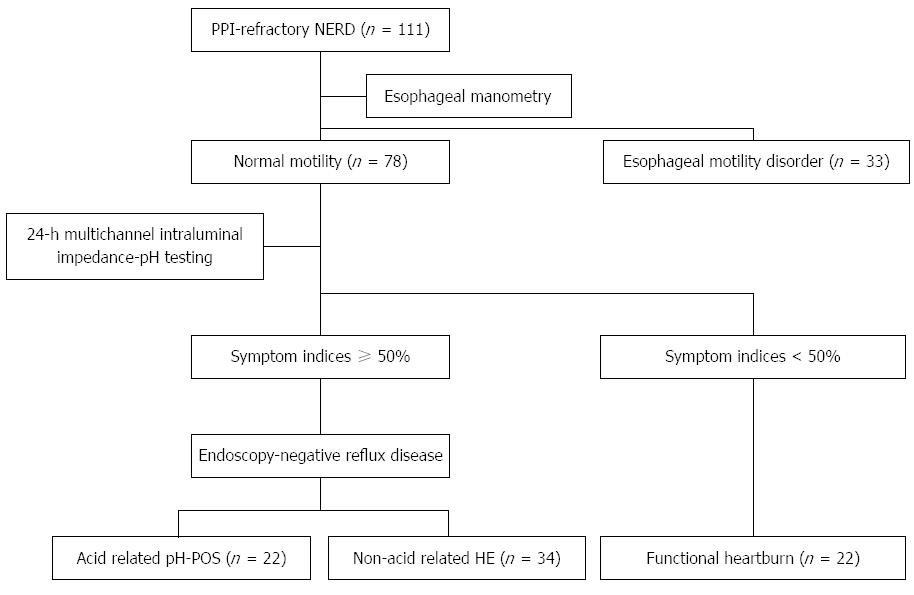
Figure 1 Based on the results obtained from intraesophageal manometry and 24-h-long intraesophageal pH/impedance monitoring, the subjects were classified into three groups according to the Rome III criteria: acid reflux-related mechanism (n = 22), non-acid reflux-related mechanism (n = 34), and functional heartburn (n = 22).
pH-POS: Excessive intraesophageal acid exposure time; HE: Hypersensitive esophagus (non-excessive esophageal acid exposure time and positive symptom index); FH: Functional heartburn; PPI: Proton pump inhibitor.
- Citation: Tamura Y, Funaki Y, Izawa S, Iida A, Yamaguchi Y, Adachi K, Ogasawara N, Sasaki M, Kaneko H, Kasugai K. Pathophysiology of functional heartburn based on Rome III criteria in Japanese patients. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(16): 5009-5016
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i16/5009.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.5009