Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2015; 21(15): 4564-4573
Published online Apr 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4564
Published online Apr 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4564
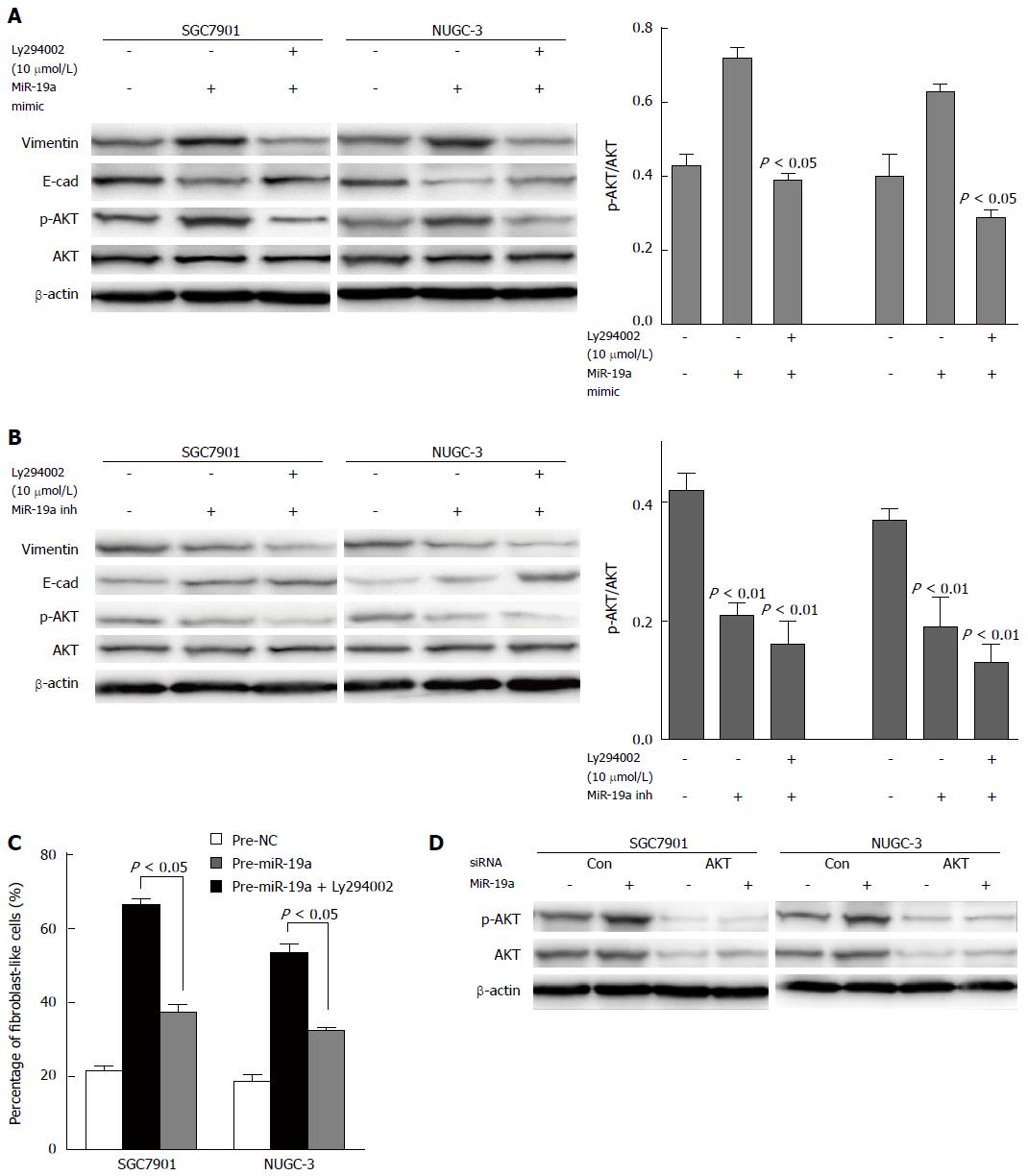
Figure 4 MiR-19a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway.
A, B: Expression profiles of p-AKT, AKT, epithelial and mesenchymal markers E-cadherin and vimentin, and β-actin in SGC-7901 and NUGC-3 cells of each group are detected by Western blot analysis. To SGC-7901 and NUGC-3 cells cultures, the PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitor Ly294002 is added, with a final concentration of 10 μmol/L. Normal control groups and groups transfected with miR-19a mimic/inhibitor are established for both SGC-7901 and NUGC-3; C: EMT phenotype in SGC7901 and NUGC-3 cells treated with miR-19a mimic in the presence of Ly294002 (10 μmol/L). The data are expressed as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments; D: Western blots showing AKT and p-AKT expression levels in cells cotransfected with miR-19a mimic and AKT siRNA.
- Citation: Lu WD, Zuo Y, Xu Z, Zhang M. MiR-19a promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition through PI3K/AKT pathway in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(15): 4564-4573
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i15/4564.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i15.4564