Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2015; 21(14): 4184-4194
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4184
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4184
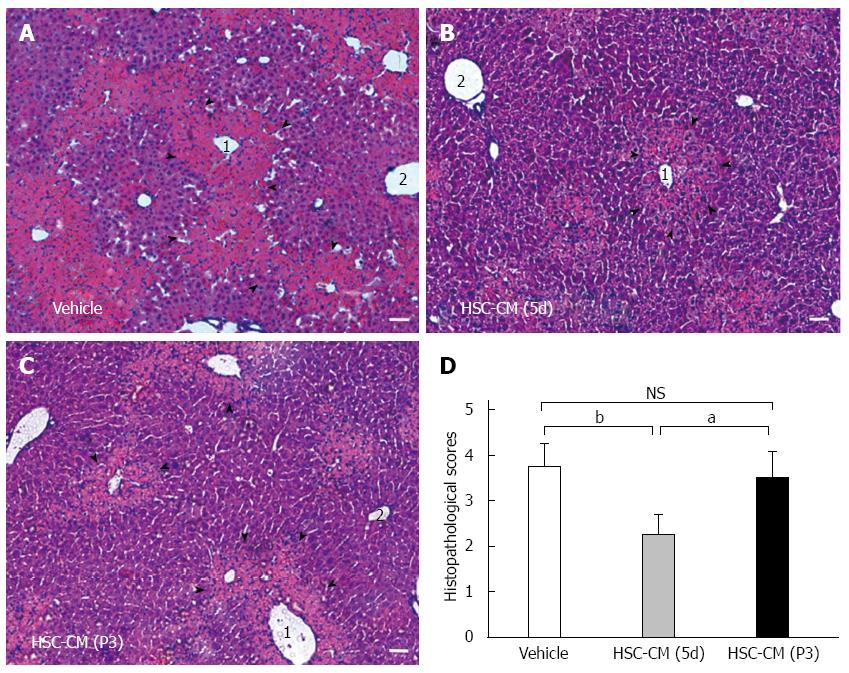
Figure 5 Hepatic stellate cell-CM (5d) treatment improves hepatocellular necrosis and immune cell infiltration in APAP-injured liver tissue.
All animals were fasted overnight before APAP treatment. Acute liver injury (ALI) mice were sacrificed 24 h after systemic vehicle or hepatic stellate cell (HSC)-CM treatment. Liver samples were subjected to histological analysis after HE staining. Microscopic low-power fields of liver tissue are shown after vehicle (A), HSC-CM (5d) (B) and HSC-CM (P3) (C) treatment. Necrotic area is indicated by arrowheads. 1: centrilobular vein, 2: portal vein. Bar = 100 μm. Scores were determined by semi-quantitative histological examination (D). Data are the mean ± SE of the mean of 10 random high-power fields per animal. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control. Bar = 100 μm. NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Chang WJ, Song LJ, Yi T, Shen KT, Wang HS, Gao XD, Li M, Xu JM, Niu WX, Qin XY. Early activated hepatic stellate cell-derived molecules reverse acute hepatic injury. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(14): 4184-4194
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i14/4184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4184