Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2015; 21(14): 4184-4194
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4184
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4184
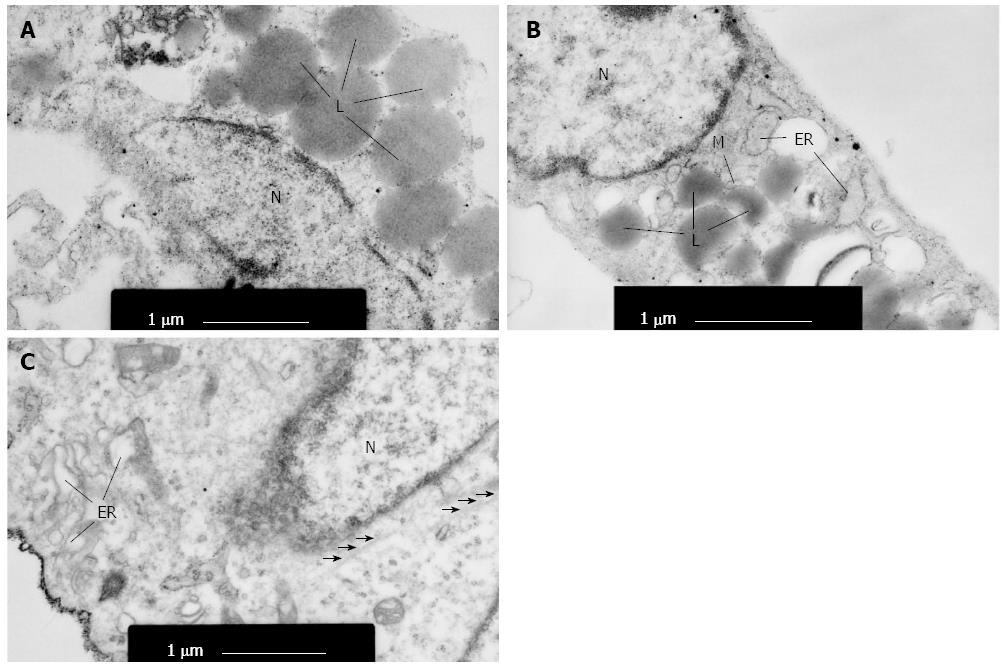
Figure 2 Ultrastructure of hepatic stellate cells observed under a transmission electron microscope.
A: HSCs contained lipid droplets (L) around the nucleus (N) after primarily cultured for 24 h; B: Primary HSCs were characterized by decreased lipid droplets and a moderate amount of rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondria (M) when cultured for 5 d; C: HSCs (P3) exhibited marked hypertrophy of rough endoplasmic reticulum and microfilaments, but no lipid droplets. Black arrows point to microfilaments. HSC: Hepatic stellate cell.
- Citation: Chang WJ, Song LJ, Yi T, Shen KT, Wang HS, Gao XD, Li M, Xu JM, Niu WX, Qin XY. Early activated hepatic stellate cell-derived molecules reverse acute hepatic injury. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(14): 4184-4194
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i14/4184.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4184