Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 7, 2015; 21(13): 3893-3903
Published online Apr 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3893
Published online Apr 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3893
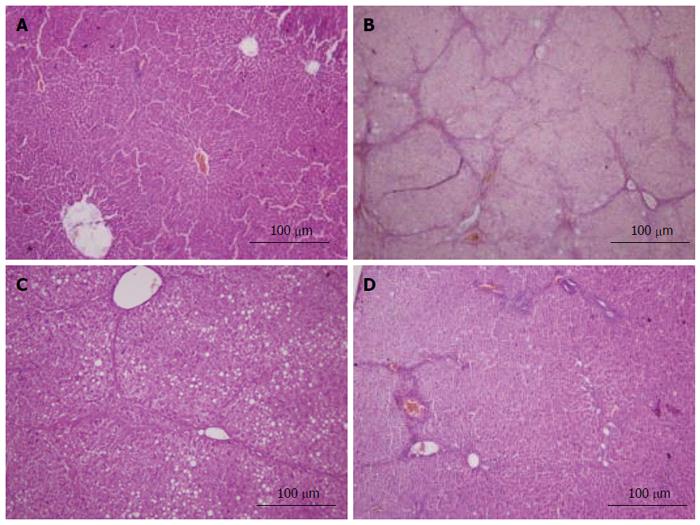
Figure 5 HE staining.
All sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (× 100). A: Liver sections of the normal group did not show histopathological changes; B: Liver sections of the model group showed liver tissue structural disorder, apoptotic cells, lymphocytic infiltration and typical pseudo-lobule; C: Liver sections of the vitamin E group showed steatosis, edema and swelling of hepatocytes, but no typical pseudo-lobule can be observed; D: Liver sections of the caffeic acid phenethyl ester (12 mg/kg) group showed spotty necrosis, steatosis, and blood sinusoids with mild congestion. The results of the other groups are not shown here.
- Citation: Li M, Wang XF, Shi JJ, Li YP, Yang N, Zhai S, Dang SS. Caffeic acid phenethyl ester inhibits liver fibrosis in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(13): 3893-3903
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i13/3893.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i13.3893