Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2015; 21(12): 3509-3518
Published online Mar 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3509
Published online Mar 28, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3509
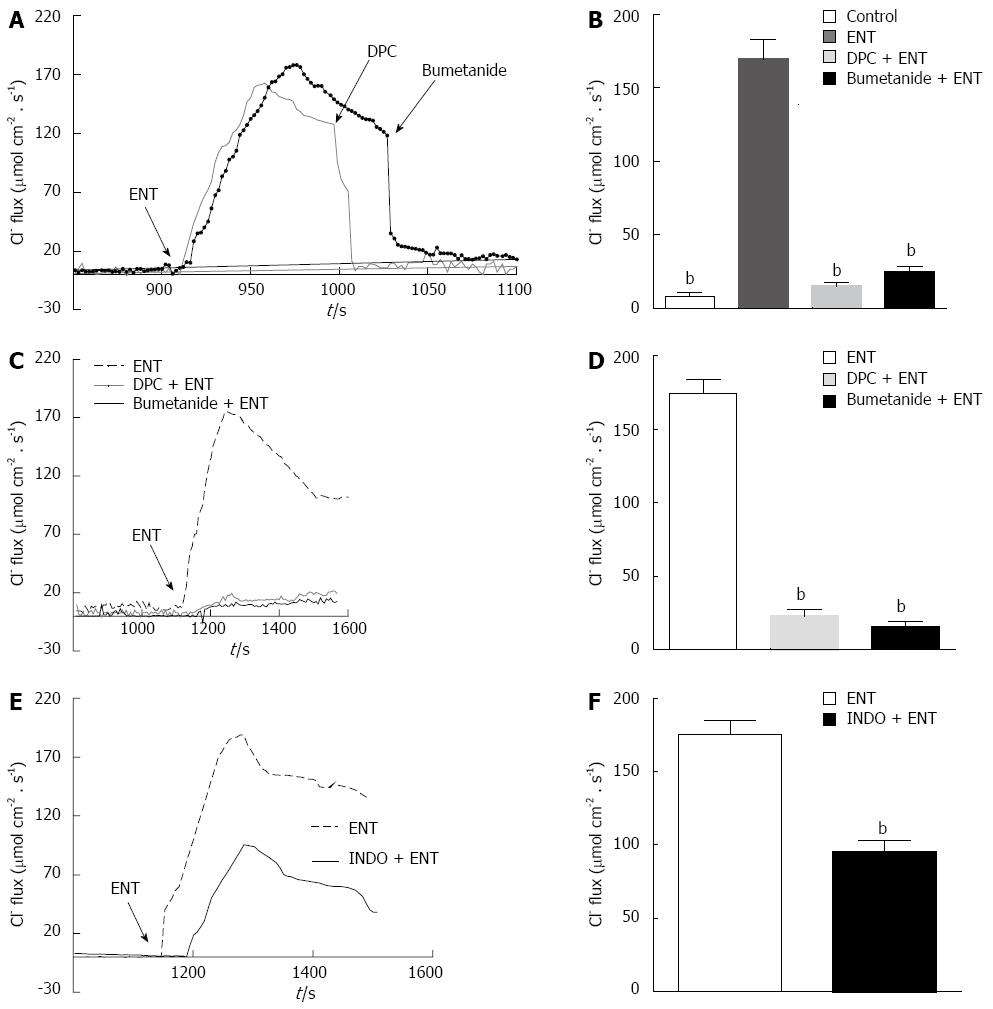
Figure 4 Utilizing scanning ion-selective electrode technique to observe the effect of entacapone on colon mucosa Cl--flux in 6-OHDA rats.
A: Application of entacapone (ENT) (200 μmol/L), diphenylamine-2, 2’-dicarboxylic acid (DPC) (1 mmol/L) and bumetanide (100 μmol/L), causing the typical performance of Cl—flux in colon specimens in 6-OHDA Parkinson’s disease (PD) rats; B: Generalization of the roles of bumetanide and DPC on the Cl--flux caused by ENT in colon specimens of 6-OHDA PD rats (n = 10); C: Application of ENT (200 μmol/L), preprocessing by bumetanide or DPC, causing the typical performance of Cl—flux in colon specimens of 6-OHDA PD rats; D: Generalization of Cl--flux caused by ENT after treatment by bumetanide and DPC in colonic specimens (n = 9); E: Application of ENT (200 μmol/L), and preprocessing by indomethacin (INDO) (10 μmol/L), causing the typical performance of Cl—flux in colon specimens in 6-OHDA PD rats; F: Generalization of the roles of INDO on the Cl--flux caused by ENT (n = 9, bP < 0.01 vs control).
- Citation: Li LS, Liu CZ, Xu JD, Zheng LF, Feng XY, Zhang Y, Zhu JX. Effect of entacapone on colon motility and ion transport in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(12): 3509-3518
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i12/3509.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i12.3509