Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2015; 21(10): 2949-2958
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2949
Published online Mar 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2949
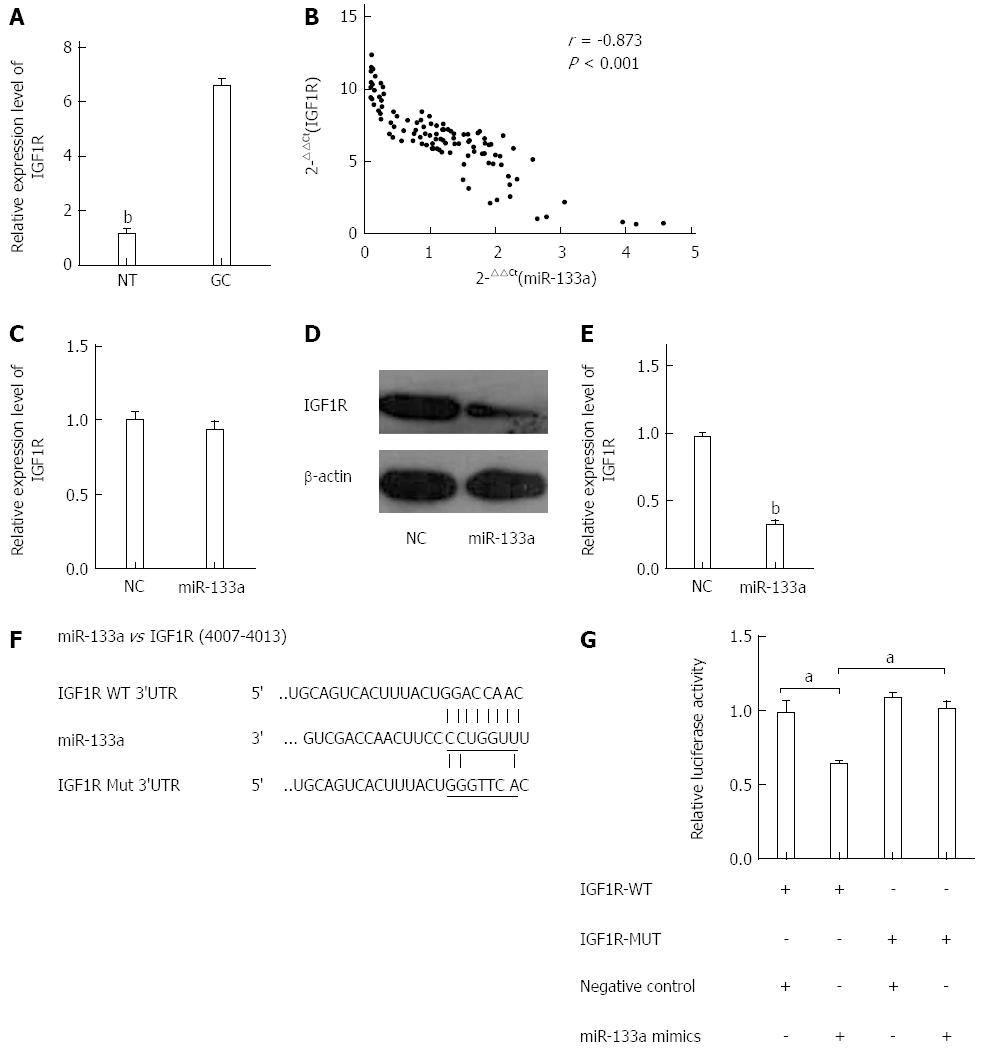
Figure 4 Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor is a direct target of miR-133a.
A: Level of insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R) mRNA was analyzed in GC tissues using quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain (qRT-PCR). The data are shown as fold change in tumor tissues relative to normal tissues (bP < 0.01 vs GC tissues); B: Expression levels of miR-133a and IGF1R were inversely correlated. The 2-ΔΔCt values of miR-133a and IGF1R mRNA were subjected to a Pearson correlation analysis (r = -0.873, P < 0.001, Pearson’s correlation); C: Level of IGF1R mRNA was examined using qRT-PCR in SGC-7901 cells 48 h after transfection with either miR-133a or negative control mimics; D: Level of IGF1R protein was examined using western blotting 48 h after transfection with miR-133a or negative control mimics; E: Relative intensity of IGF1R protein expression after normalization to β-actin (bP < 0.01 vs control); both D and E indicate that the level of IGF1R protein was significantly reduced compared with that of the negative control; F: Interaction between miR-133a and 3’ UTR of IGF1R was predicted using TargetScan. Here, “IGF1R Mut 3’UTR” indicates the IGF1R 3’ UTR with a mutation in the miR-133a binding site; G: Luciferase activity of a reporter containing a wild-type IGF1R 3’ UTR or a mutant IGF1R 3’ UTR are shown in the bar graph (aP < 0.05 vs control). All data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments.
- Citation: Gong Y, Ren J, Liu K, Tang LM. Tumor suppressor role of miR-133a in gastric cancer by repressing IGF1R. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(10): 2949-2958
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i10/2949.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i10.2949