Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2015; 21(1): 196-213
Published online Jan 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.196
Published online Jan 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.196
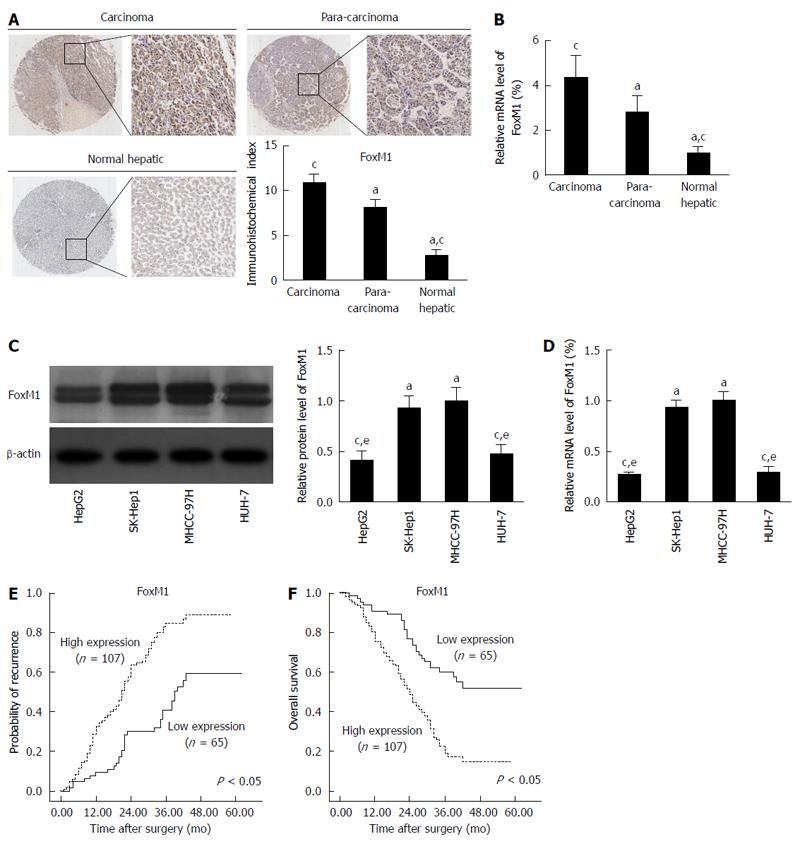
Figure 1 Forkhead box protein M1 overexpression correlates significantly with hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis.
A: Immunohistochemistry was used to detect forkhead box protein M1 (FoxM1) expression in normal liver, para-carcinoma, and carcinoma (HCC) tissues (aP < 0.05 vs carcinoma; cP < 0.05 vs para-carcinoma); B: Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis of FoxM1 mRNA expression in normal liver, para-carcinoma, and carcinoma (HCC) tissues (aP < 0.05 vs carcinoma; cP < 0.05 vs para-carcinoma). Glyceraldehyde-3-phospate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA was used for normalization; C: Western blot analysis of FoxM1 expression in human HCC cell lines (aP < 0.05 vs HepG2; cP < 0.05 vs SK-Hep1; eP < 0.05 vs MHCC-97H); D: qRT-PCR analysis of FoxM1 mRNA expression in human HCC cell lines (aP < 0.05 vs HepG2; cP < 0.05 vs SK-Hep1; eP < 0.05 vs MHCC-97H). GAPDH mRNA was used for normalization; E and F: Kaplan-Meier analysis of the correlation between FoxM1 expression level and recurrence or overall survival of HCC patients.
- Citation: Meng FD, Wei JC, Qu K, Wang ZX, Wu QF, Tai MH, Liu HC, Zhang RY, Liu C. FoxM1 overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(1): 196-213
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i1/196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.196