Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2014; 20(7): 1822-1832
Published online Feb 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1822
Published online Feb 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1822
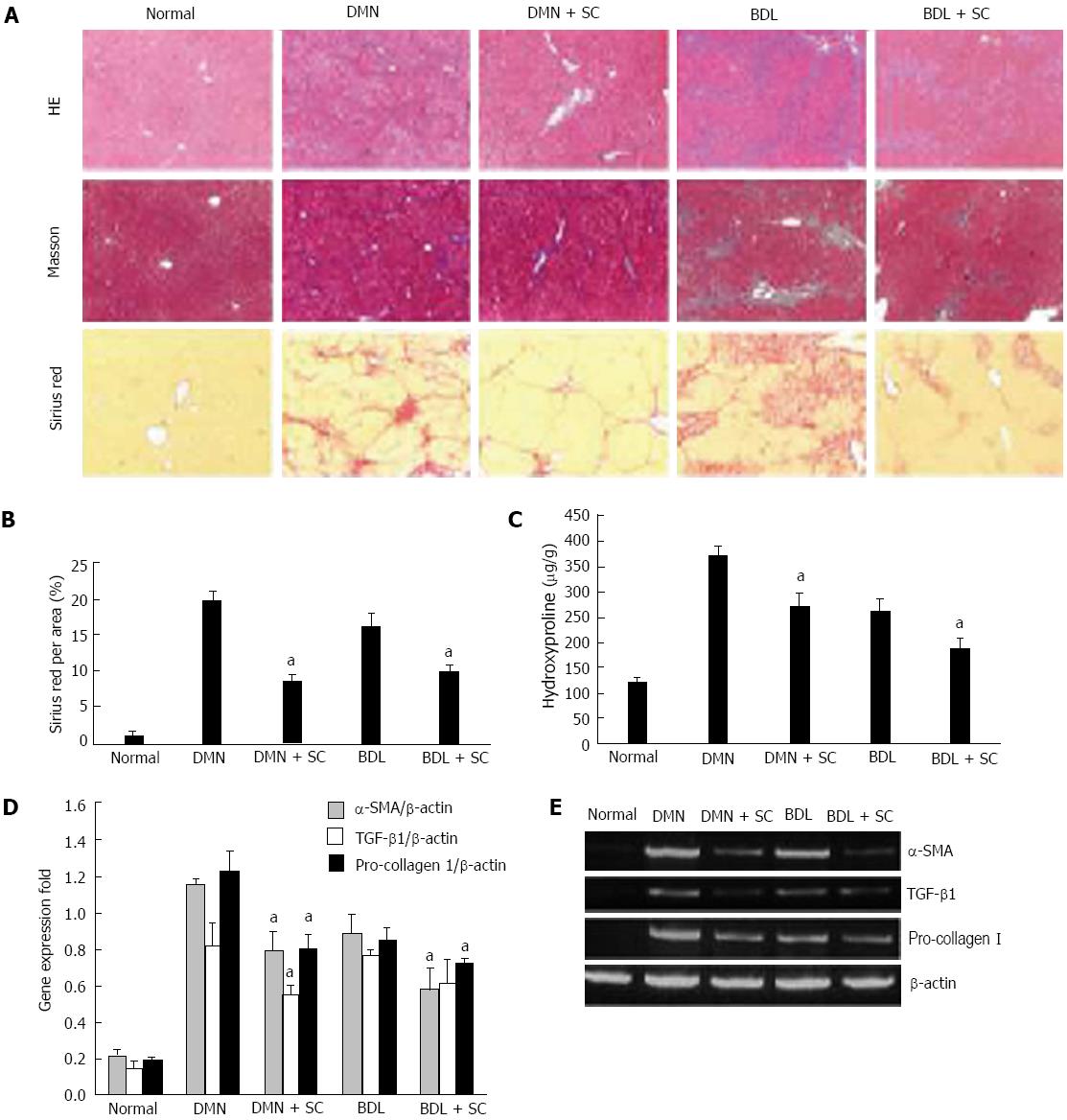
Figure 2 Sophocarpine attenuates hepatic fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine or bile duct ligation in rats.
DMN and BDL were used to construct two types of hepatic fibrosis models to evaluate the therapeutic effect of sophocarpine. A: Liver fibrosis in each group was assessed by HE (× 40), Masson’s trichrome (× 40) and Sirius red staining (× 40); B: The percentage of Sirius-red in fibrotic livers was quantified using an image analysis system (aP < 0.05); C: The amount of hydroxyproline in fibrotic livers was detected in the sophocarpine-treated group compared with each model group (aP < 0.05); D, E: Real-time RT-PCR was employed to examine the expression of α-SMA, TGF-β and pro-collagen I in fibrotic livers following sophocarpine administration compared with the control models (aP < 0.05 by two-tailed Student’s t test). DMN: Dimethylnitrosamine; BDL: Bile duct ligation; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; RT-PCR: Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction; SMA: Smooth muscle actin.
- Citation: Qian H, Shi J, Fan TT, Lv J, Chen SW, Song CY, Zheng ZW, Xie WF, Chen YX. Sophocarpine attenuates liver fibrosis by inhibiting the TLR4 signaling pathway in rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(7): 1822-1832
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i7/1822.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1822