Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2014; 20(7): 1807-1821
Published online Feb 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1807
Published online Feb 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1807
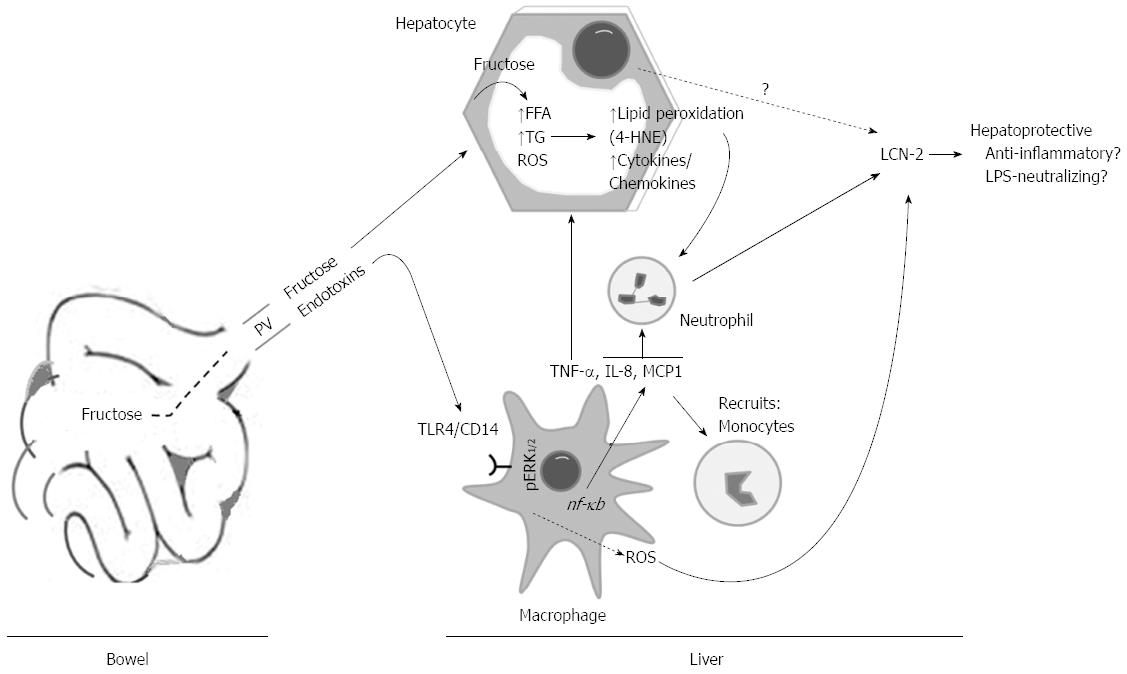
Figure 8 Hypothetical model of the mechanism thereby lipocalin-2 was produced in high fructose-induced rat fatty liver.
Ingested fructose is delivered into the liver via portal vein. Once in liver, hepatocytes transformed fructose into FFAs and TGs. In addition, the chronic fructose consumption facilitates the influx of endotoxins LPS into the liver. Endotoxins stimulate Kupffer cells which, in turn, release ROS and cytokines. This results in recruitment of more neutrophil granulocytes and monocytes to the liver. As a result of fat accumulation in hepatocytes, lipid peroxidation end products (e.g., 4-HNE), iNOS and other cytokines/chemokines will be produced, which could recruit neutrophil granulocytes to the liver. LCN-2 could act as hepatoprotective protein. PV: Portal vein; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; LCN-2: Lipocalin-2.
- Citation: Alwahsh SM, Xu M, Seyhan HA, Ahmad S, Mihm S, Ramadori G, Schultze FC. Diet high in fructose leads to an overexpression of lipocalin-2 in rat fatty liver. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(7): 1807-1821
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i7/1807.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1807