Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2014; 20(6): 1554-1564
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1554
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1554
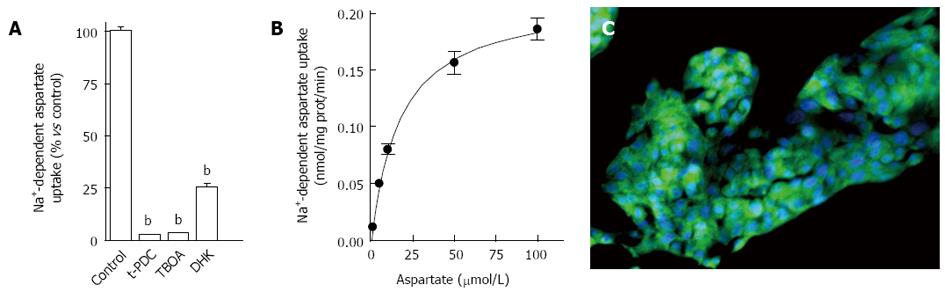
Figure 1 Characterization of Na+-dependent D-[3H]-aspartate uptake in HepG2 hepatoblastoma cells.
A: D-[3H]-aspartate (30 nmol/L) uptake was measured after 6 min incubation with intact HepG2 cells treated with vehicle (controls), t-PDC (1 mmol/L), TBOA (1 mmol/L) or DHK (100 μmol/L) for 15 min. Data shown are mean ± SE of at least three independent experiments performed in quadruplicate. bP < 0.001 as compared to control (paired student t-test); B: Saturation isotherms for D-[3H]-aspartate (1-100 μmol/L) uptake measured in HepG2 cells. Data shown correspond to mean values with SE from quadruplicate measures on four independent series; C: Immunofluorescence detection of EAAT2 transporter on HepG2 cells using specific polyclonal antibody. Immunoreactivity was visualized using a FITC-conjugated rabbit anti-goat antibody, and cell nuclei appear in blue (DNA staining with DAPI) (original magnification × 200). t-PDC: L-trans-pyrrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylic acid; TBOA: Threo-beta-benzyloxyaspartate; DHK: Dihydrokainic acid; DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole.
- Citation: Najimi M, Stéphenne X, Sempoux C, Sokal E. Regulation of hepatic EAAT-2 glutamate transporter expression in human liver cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(6): 1554-1564
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i6/1554.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1554