Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2014; 20(6): 1537-1543
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1537
Published online Feb 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1537
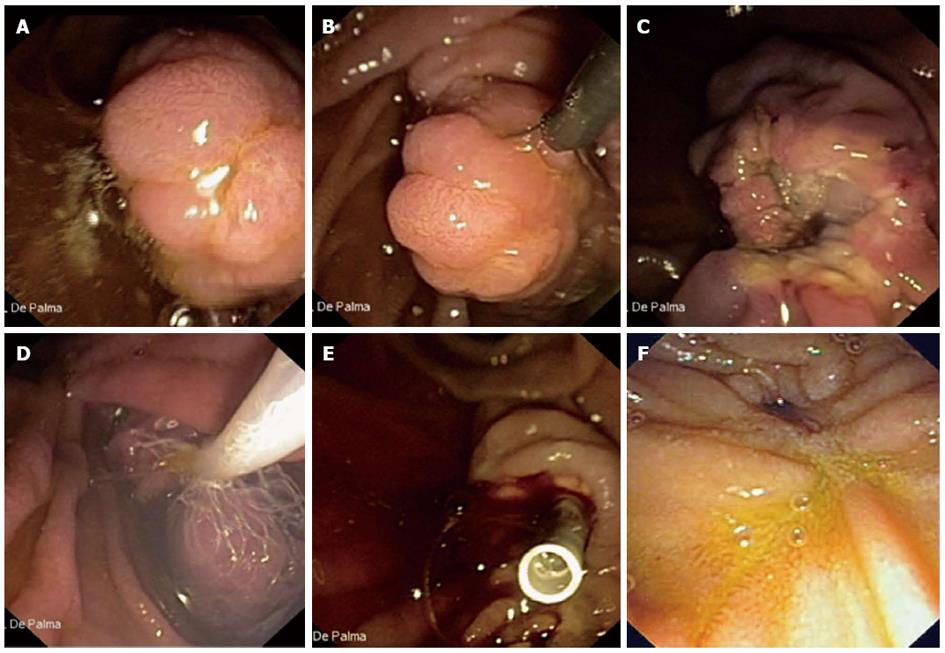
Figure 1 Aggressive efforts to retrieve all resected tissue in all patients for histopathologic evaluation are mandatory.
A: Endoscopic view of a 3 cm neoplastic lesion of the major papilla; B: The lesion is entirely entrapped by the endoscopic snare; C: The lesion is completely resected (en-bloc resection); D: The resected specimen is retrieved by a Roth Net© device (US Endoscopy, Mentor, OH, United States); E: A plastic stent is implanted into the main pancreatic duct to prevent post-papillectomy pancreatitis; F: Duodenal view 6 mo after papillectomy. No evidence of recurrent disease is observed.
- Citation: Palma GDD. Endoscopic papillectomy: Indications, techniques, and results. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(6): 1537-1543
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i6/1537.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i6.1537