Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2014; 20(5): 1298-1304
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1298
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1298
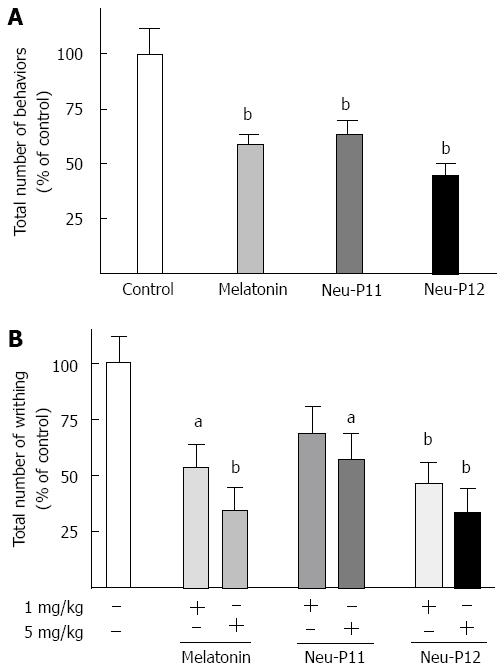
Figure 3 Melatonin, Neu-P11 and Neu-P12 decreased the number of pain-related behaviors.
A: Melatonin, Neu-P11 and Neu-P12 (all at 25 mg/kg, ip) decreased the number of pain-related behaviors in the capsaicin-induced visceral pain test 15 min after drug administration; B: Melatonin, Neu-P11 and Neu-P12 (all 5 at mg/kg, ip) decreased the number of pain-related behaviors in the writhing test 15 min after drug administration. Data are mean ± SE (n = 6-10). aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01 vs control.
- Citation: Chen C, Fichna J, Laudon M, Storr M. Antinociceptive effects of novel melatonin receptor agonists in mouse models of abdominal pain. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(5): 1298-1304
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i5/1298.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1298