Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2014; 20(5): 1127-1138
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127
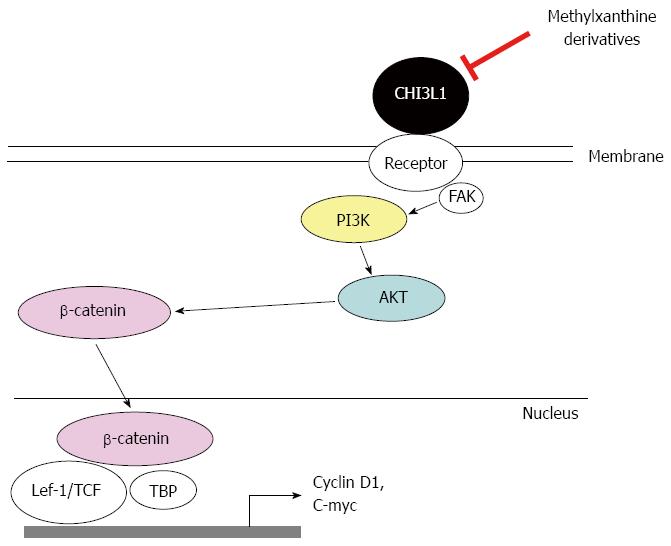
Figure 4 Schematic representation of chitinase 3-like 1-associated β-catenin activation signaling pathway, which is inhibited by methylxanthine derivatives.
Binding of extracellular chitinase 3-like 1 (CHI3L1) to a putative receptor on plasma membrane activates the intracellular phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (AKT) signaling pathway, which leads to β-catenin activation by translocating this protein from cytoplasm into nucleus. Methylxanthine derivatives, including caffeine, pentoxifylline and theophylline, directly down-regulate CHI3L1 mRNA expression and inhibit CHI3L1 protein functions, leading to reduced CHI3L1-associated AKT activation and prevent down-stream β-catenin nuclear translocation with different degrees of efficacy.
- Citation: Lee IA, Kamba A, Low D, Mizoguchi E. Novel methylxanthine derivative-mediated anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(5): 1127-1138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i5/1127.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127