Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2014; 20(5): 1127-1138
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127
Published online Feb 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127
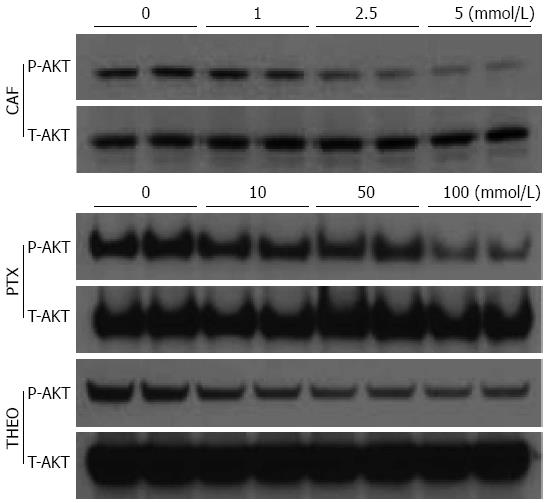
Figure 2 Caffeine, pentoxifylline and theophylline suppress protein kinase B signaling pathway activation in mouse colonic epithelial cells.
CMT93 mouse colonic epithelial cells were stimulated with caffeine (CAF) (0, 1, 2.5 or 5 mmol/L), pentoxifylline (PTX) or theophylline (THEO) (0, 10, 50 or 100 mmol/L) for 48 h. Twenty five micro grams of total protein were resolved using SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and analyzed by Western blot using anti-phospho/total protein kinase B (AKT) Abs purchased from cell signaling technology (Danvers, MA, United States) .
- Citation: Lee IA, Kamba A, Low D, Mizoguchi E. Novel methylxanthine derivative-mediated anti-inflammatory effects in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(5): 1127-1138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i5/1127.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i5.1127