Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18284-18295
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18284
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18284
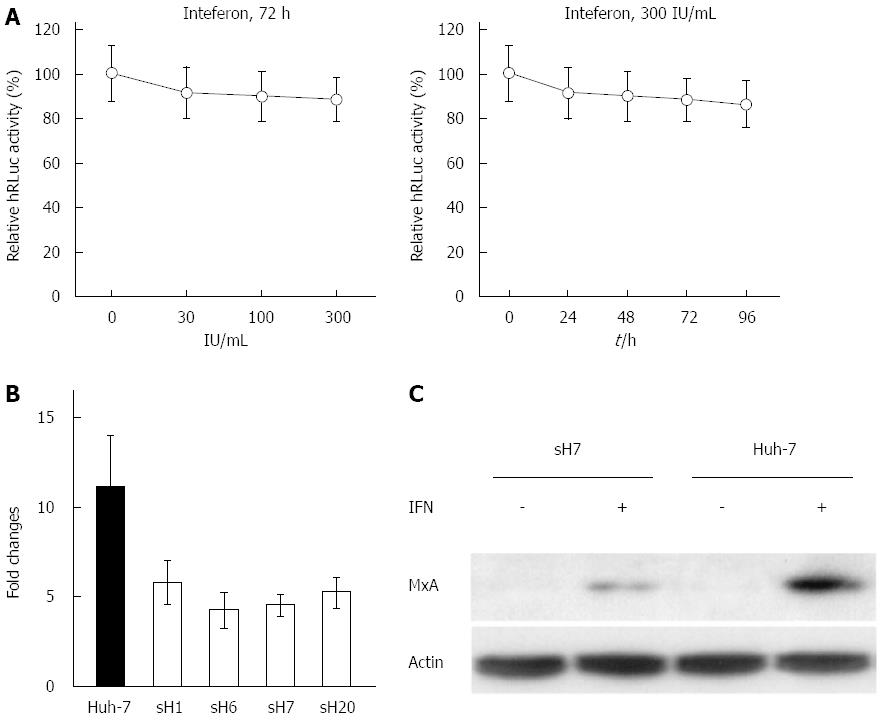
Figure 5 Resistance of hepatitis C virus replicon to interferon-α2b in sH7 cells.
A: The replication of hepatitis C virus (HCV) replicon was not blocked by interferon (IFN)α2b. The sH7 cells, in which HCV replicon was stably replicated along with humanized Renilla luciferase (hRLuc) expression, were treated with increasing doses of IFNα2b for different durations. The replication of HCV replicon was not blocked by IFNα2b up to 300 IU/mL for 96 h. The relative light units were normalized to those in untreated sH7 wells as a control; B: Real-time PCR of MxA mRNA in Huh-7 cells and HCV replicon cell lines treated with IFNα2b. The fold change of MxA mRNA in Huh-7 cells after IFN treatment was much higher than fold changes in HCV replicon stably transfected cell lines after IFN treatment; C: MxA protein in sH7 and Huh-7 cells treated with IFNα2b. MxA protein level was elevated by IFNα2b in both Huh-7 and sH7 cells, whereas no MxA was detected in these two types of cells without IFN stimulation. Additionally, the level of MxA protein was greater in parental Huh-7 cells than in sH7 cells in which HCV replicon was stably transfected.
- Citation: Cheng X, Gao XC, Wang JP, Yang XY, Wang Y, Li BS, Kang FB, Li HJ, Nan YM, Sun DX. Tricistronic hepatitis C virus subgenomic replicon expressing double transgenes. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18284-18295
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18284.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18284