Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18271-18283
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18271
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18271
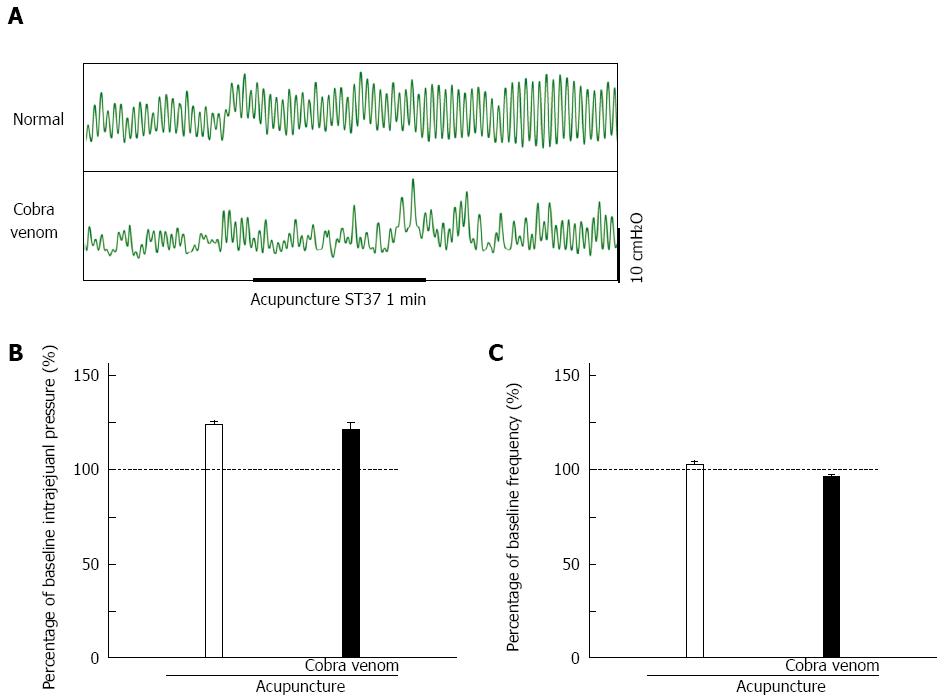
Figure 4 Effect of cobra venom on the regulation of jejunal motility by manual acupuncture at ST37.
A: Representative traces of jejunal motility without and with cobra venom; B: Cobra venom did not inhibit the improved intrajejunal pressure caused by acupuncture at ST37 (unpaired t-test, n = 20). Intrajejunal pressure was normalized by baseline, shown as the dashed line; C: Cobra venom had no effect on ST37 acupuncture-mediated regulation of frequency of jejunal motility (unpaired t-test, n = 20). Frequency was normalized by baseline, as denoted by the dashed line.
- Citation: Qin QG, Gao XY, Liu K, Yu XC, Li L, Wang HP, Zhu B. Acupuncture at heterotopic acupoints enhances jejunal motility in constipated and diarrheic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18271-18283
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18271.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18271