Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18228-18239
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18228
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18228
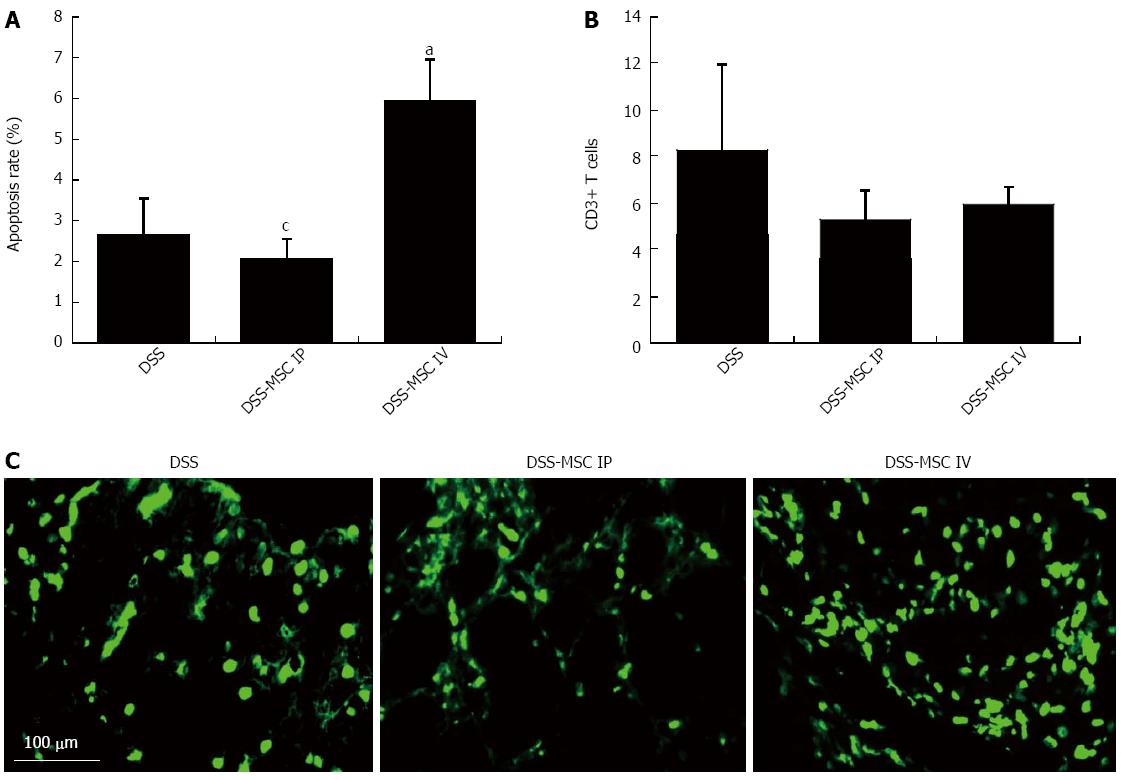
Figure 6 Intravenous administration of mesenchymal stem cells induced T cell apoptosis.
A: Apoptosis rate. TUNEL-positive mononuclear cells were significantly more frequent in the DSS-MSC IV group when compared to the DSS-MSC IP and DSS groups; B: Apoptotic T cells were detected by immunohistochemical staining with anti-CD3 antibody; C: TUNEL assay showing fluorescent apoptotic cells after DSS administration. aP < 0.05 vs DSS group; cP < 0.05 vs DSS-MSC IV, n = 5 mice/group. Scale bar: 100 μm. TUNEL: Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUDP-biotin nick end labeling; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; MSC: Mesenchymal stem cell.
-
Citation: Gonçalves FDC, Schneider N, Pinto FO, Meyer FS, Visioli F, Pfaffenseller B, Lopez PLDC, Passos EP, Cirne-Lima EO, Meurer L, Paz AH. Intravenous
vs intraperitoneal mesenchymal stem cells administration: What is the best route for treating experimental colitis? World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18228-18239 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18228.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18228