Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2014; 20(48): 18189-18198
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18189
Published online Dec 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18189
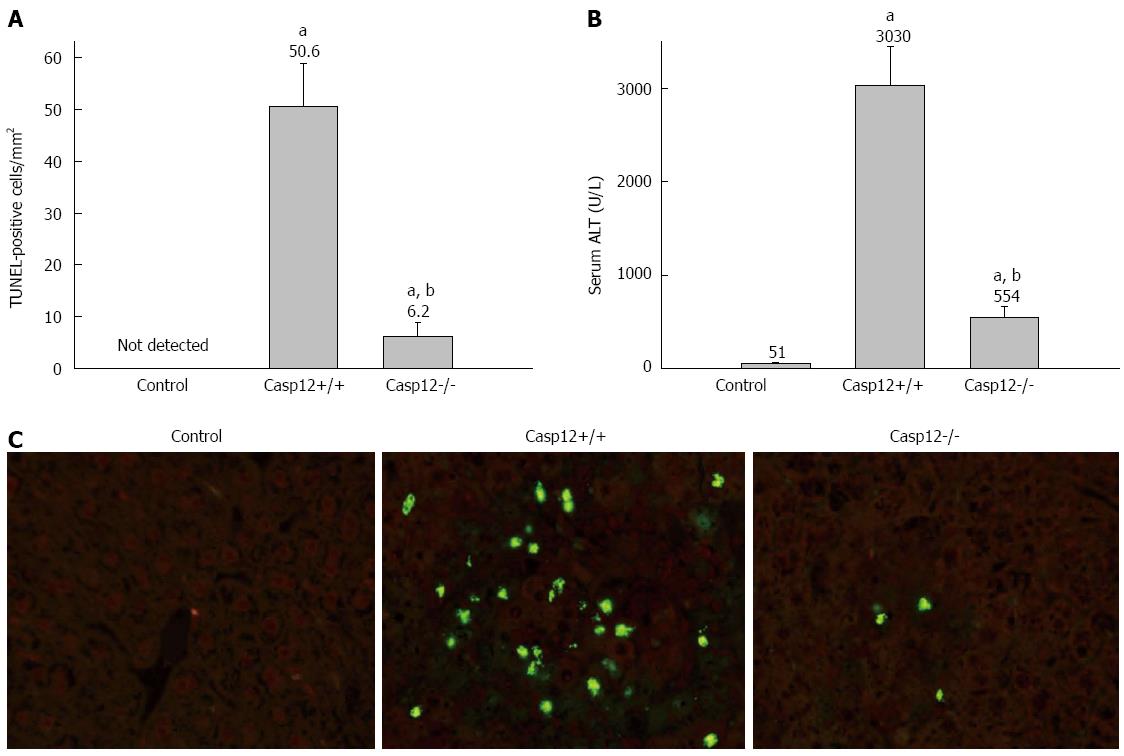
Figure 5 Attenuated carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic apoptosis and liver injury in caspase-12-/- mice.
A: Terminal transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling (TUNEL) staining to evaluate carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in caspase-12-/- mice. Five randomly selected fields at 200× magnification were evaluated for each tissue section. The numbers of apoptotic cells were counted as TUNEL-positive cells/mm2. Values are mean ± SE, n = 8; aP < 0.05 vs controls, cP < 0.05 vs caspase-12+/+; B: CCl4-induced liver injury as measured by serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels. Values are mean ± SE, n = 8; eP < 0.05 vs controls, gP < 0.05 vs caspase-12+/+ mice; C: Representative sections of TUNEL staining under fluorescence microscope (200 ×). TUNEL-positive cells were identified by the nuclear fluorescence staining.
- Citation: Liu H, Wang Z, Nowicki MJ. Caspase-12 mediates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatocyte apoptosis in mice. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(48): 18189-18198
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i48/18189.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i48.18189