Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2014; 20(47): 17924-17931
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17924
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17924
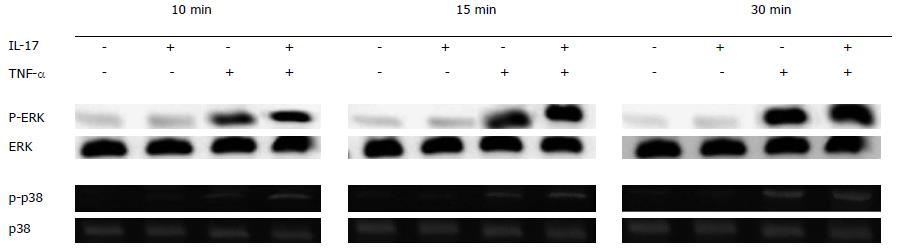
Figure 2 p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase phosphorylation levels.
When interleukin (IL)-17 and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α were used separately, the phosphorylation levels of p38 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) were very low. However, when IL-17 and TNF-α were combined together, the phosphorylation levels of p38 and ERK improved significantly, and the longer IL-17 and TNF-α were combined together, the stronger the phosphorylation became.
- Citation: Wang YL, Fang M, Wang XM, Liu WY, Zheng YJ, Wu XB, Tao R. Proinflammatory effects and molecular mechanisms of interleukin-17 in intestinal epithelial cell line HT-29. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(47): 17924-17931
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i47/17924.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17924