Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2014; 20(47): 17839-17850
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17839
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17839
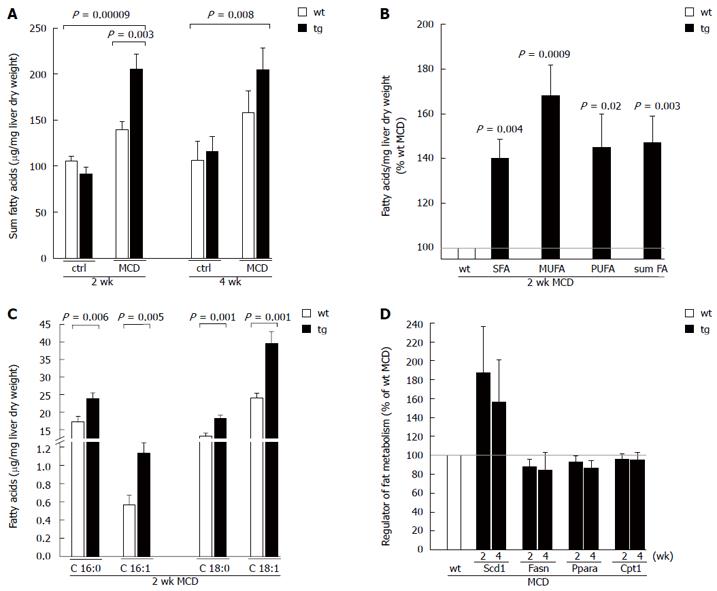
Figure 2 p62 alters the fatty acid pattern.
A: Sum of all fatty acids in mice fed the methionine-choline deficient (MCD) or ctrl diet for two and four weeks. Liver tissues were lyophilized, lipids were hydrolyzed, and fatty acids (FA) were analyzed by gas-chromatography mass-spectrometry (GC-MS); B: Sum of the saturated fatty acids (SFA), monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFA), polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), and all fatty acids (sum FA) from animals fed the MCD diet for two weeks are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 9-12). Data are displayed as the percentage of MCD-fed wild-type mice, which were set to 100%, each; C: Palmitic acid (C16:0), palmitoleic acid (C16:1), stearic acid (C18:0), and oleic acid (C18:1) are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 9-12); D: Relative hepatic mRNA expression of stearoyl-CoA desaturase (SCD) 1, fatty acid synthase (FASN), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor a (PPARa), and carnitine palmitoyl transferase (CPT) 1a from mice fed the MCD diet for two and four weeks were normalized against the housekeeping gene 18S and are shown as the percentage of MCD-fed wild-type mice, which were set to 100%, each. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 10-12). tg: Transgenic; wt: Wild-type; ctrl: Control.
- Citation: Simon Y, Kessler SM, Gemperlein K, Bohle RM, Müller R, Haybaeck J, Kiemer AK. Elevated free cholesterol in a p62 overexpression model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(47): 17839-17850
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i47/17839.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17839