Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2014; 20(47): 17839-17850
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17839
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17839
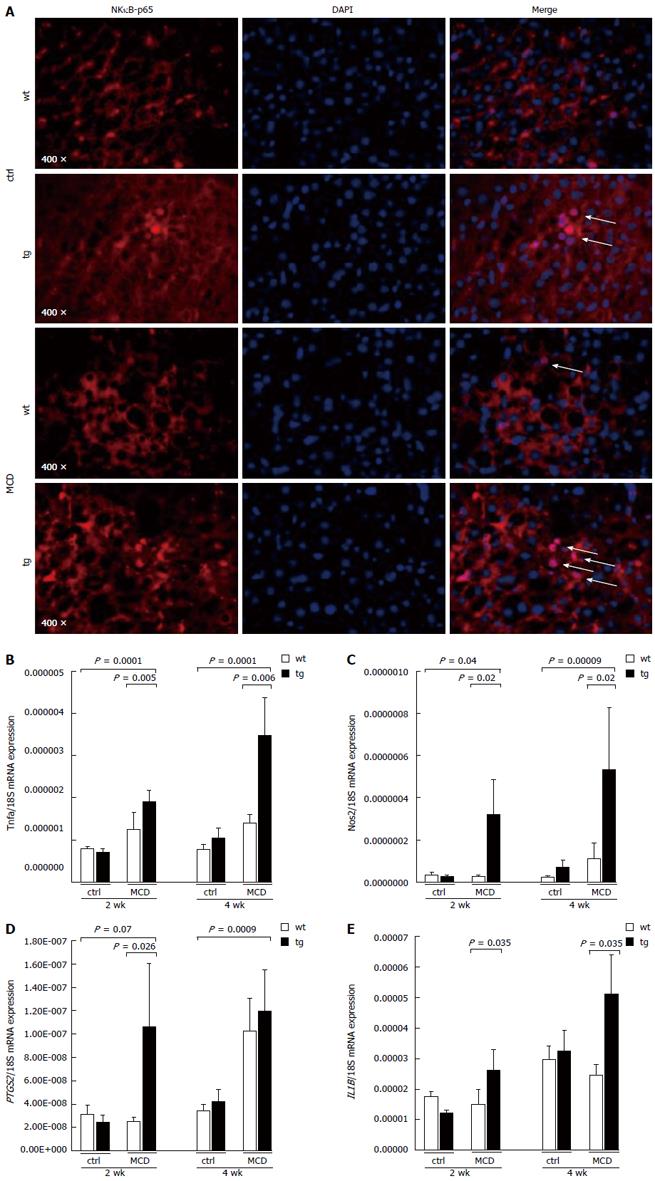
Figure 1 p62 expression amplifies inflammation.
A: Immunofluorescent staining with anti-nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB)-p65 (red, left panel), 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) for nuclei (blue, middle panel), and merge (right panel) shows activation of NF-κB after four weeks on the methionine-choline deficient (MCD) diet through p65 translocation to the nucleus (white arrows) (original magnification: × 400); B-E: Gene expression analysis from quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) of NF-κB target genes with tumor necrosis factor (TNF) (B), inducible nitric oxide synthase 2 (NOS2) (C), prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS/COX2) (D), and interleukin 1B (IL-1B) (E) from whole livers are expressed as a ratio against the housekeeping gene, 18S. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 10-12). ctrl: Control; wt: Wild type; tg: Transgenie.
- Citation: Simon Y, Kessler SM, Gemperlein K, Bohle RM, Müller R, Haybaeck J, Kiemer AK. Elevated free cholesterol in a p62 overexpression model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(47): 17839-17850
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i47/17839.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17839