Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2014; 20(47): 17699-17708
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17699
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17699
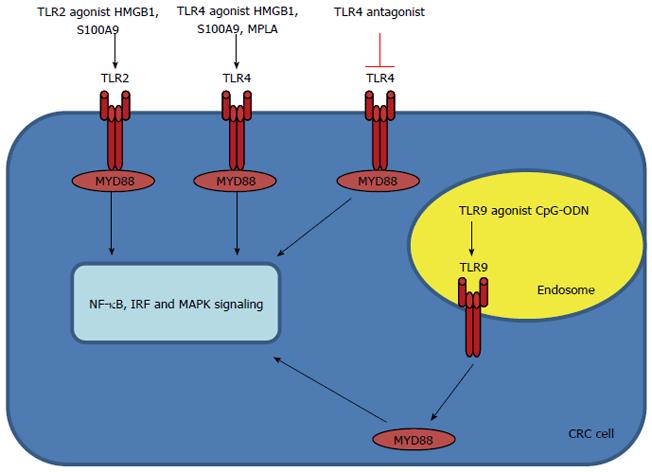
Figure 2 Toll-like receptors in colorectal cancer and therapeutics.
Toll-like receptor (TLR) agonists play a fundamental role in activating innate and adaptive immune responses. The TLR2 and TLR4 agonists HMGB1 and S100A9 have been proposed as potential biomarkers for colorectal cancer (CRC). The TLR4 agonist monophosphoryl lipid (MPL) A is approved for use in several vaccines as an adjuvant. TLR9 agonist, commonly referred to as CpG-ODN, has been added to the arsenal of anti-cancer drugs as monotherapy or in combination with chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other immunotherapeutic approaches. Activated TLR2, TLR4 and TLR9 recruit MYD88, with activation of NF-κB, IRF, and MAPK signaling, leads to inflammation, immune regulation, survival, proliferation and tumorigenesis. MAPK: Mitogen-associated protein kinase; IRF: Interferon regulatory factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor (NF)-κB.
- Citation: Li TT, Ogino S, Qian ZR. Toll-like receptor signaling in colorectal cancer: Carcinogenesis to cancer therapy. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(47): 17699-17708
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i47/17699.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17699