Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2014; 20(46): 17541-17551
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17541
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17541
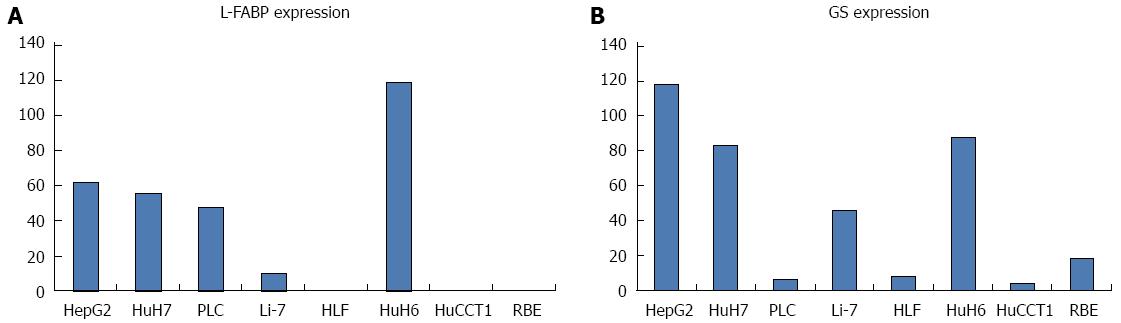
Figure 4 Expression levels of liver fatty acid-binding protein and glutamine synthetase mRNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma cell lines.
A: Among six hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell lines examined, HepG2, HuH7, PLC, and HuH6 showed higher expression of liver fatty acid-binding protein (L-FABP). However, Li-7 and HLF showed lower expression of L-FABP. In particular, L-FABP expression was almost undetectable in HLF. Expression levels of L-FABP were very low in two CC cell lines examined (HuCCT1 and RBE); B: No obvious correlation was observed between L-FABP and glutamine synthetase expression in HCC cell lines.
- Citation: Inoue M, Takahashi Y, Fujii T, Kitagawa M, Fukusato T. Significance of downregulation of liver fatty acid-binding protein in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(46): 17541-17551
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i46/17541.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17541