Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2014; 20(46): 17416-17425
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17416
Published online Dec 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17416
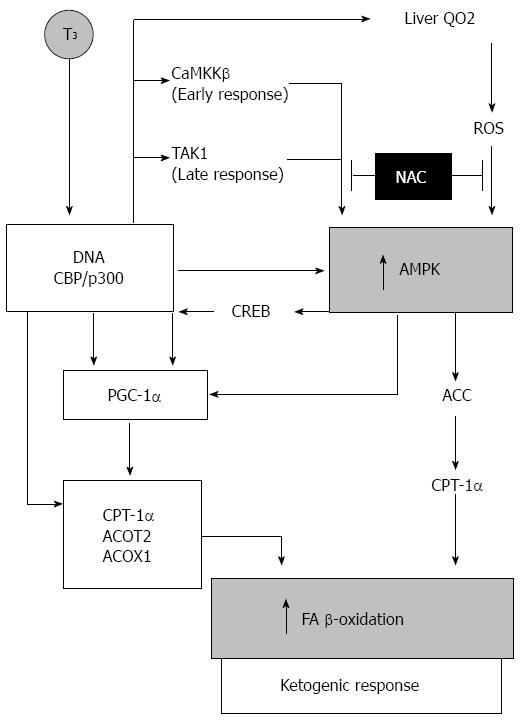
Figure 4 Schematic representation of T3 signaling related to AMPK upregulation and consequent fatty acid oxidation enhancement.
ACC: Acetyl-CoA carboxylase; ACOT2: acyl-CoA thioesterase 2; ACOX1: acyl-CoA oxidase 1; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CaMKKβ: Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-β; CBP/p300: CREB-binding protein; CPT-1α: Carnitine palmitolytransferase-1α; CREB: cAMP-response element-binding protein; FA: Fatty acid; PGT-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α; QO2: Rate of oxygen consumption; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TAK1: Transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase-1.
- Citation: Videla LA, Fernández V, Cornejo P, Vargas R, Morales P, Ceballo J, Fischer A, Escudero N, Escobar O. T3-induced liver AMP-activated protein kinase signaling: Redox dependency and upregulation of downstream targets. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(46): 17416-17425
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i46/17416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i46.17416