Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2014; 20(45): 17247-17253
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17247
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17247
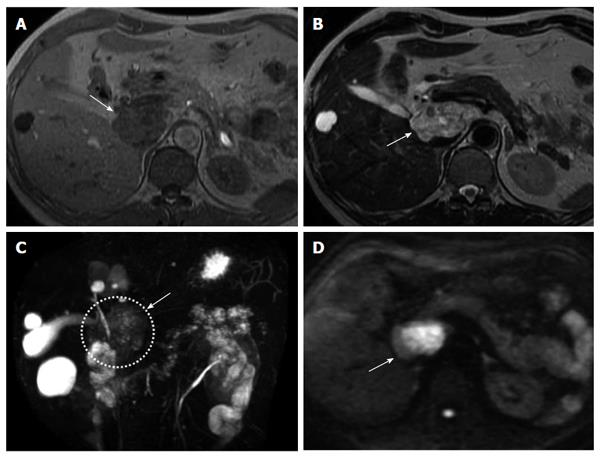
Figure 6 Findings of patient #4.
A: Findings of T1-weighted imaging on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). T1-weighted imaging of patient showed a higher intensity than free water (arrow); B: Findings of T2-weighted imaging on MRI. T2-weighted imaging of patient showed a lower intensity than free water (arrow); C: Findings of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). MRCP of patient showed a lower intensity than free water (arrow); D: Findings of diffusion-weighted imaging on MRI (arrow). Diffusion-weighted imaging of three patients showed a higher intensity than free water. The cystic lesions showed high intense signal in the central part and iso-intense in the periphery.
- Citation: Terakawa H, Makino I, Nakagawara H, Miyashita T, Tajima H, Kitagawa H, Fujimura T, Inoue D, Kozaka K, Gabata T, Ohta T. Clinical and radiological feature of lymphoepithelial cyst of the pancreas. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(45): 17247-17253
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i45/17247.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17247