Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2014; 20(45): 17049-17064
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049
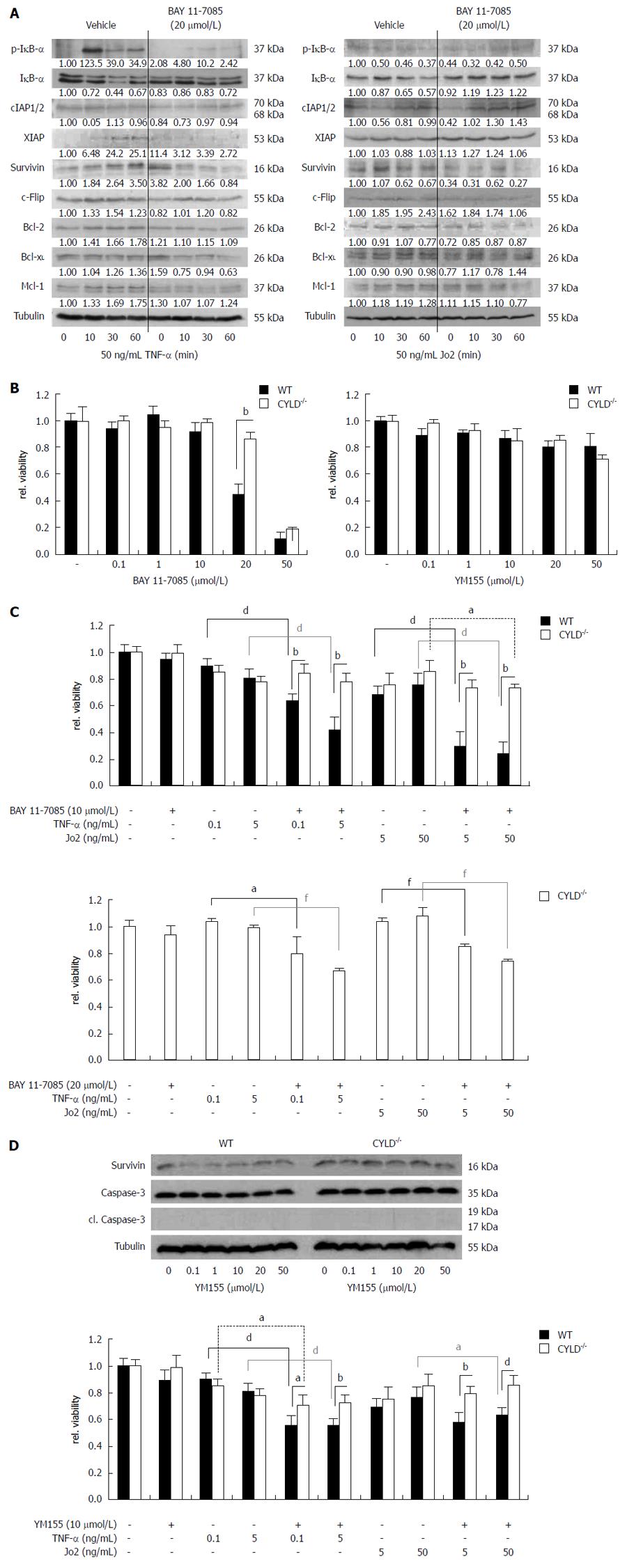
Figure 5 Nuclear factor-κB and survivin inhibition sensitized primary murine hepatocytes towards receptor-mediated cell death.
A: Western blot analysis for nuclear factor (NF)-κB regulated gene expression after tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-R (left panel) and CD95-R (right panel) triggering of CYLD-/- primary murine hepatocytes (PMH) 4 h pre-incubated with BAY 11-7085; B: 24 h treatment of WT and CYLD-/- PMH with increasing concentrations of BAY 11-7085 (left panel) and YM155 (right panel); C: WT and CYLD-/- PMH were pre-incubated with 10 μmol/L BAY-11 7085 for 4 h. Afterwards PMH were treated for 24 h in combination with TNF-α or Jo2 as indicated (upper panel). Pre-incubation of CYLD-/- PMH with 20 μmol/L BAY-11 7085 and following TNF-α or Jo2 treatment (lower panel); D: Western blot analysis for survivin expression in WT and CYLD-/- PMH 24 h after treatment with YM155 as indicated (upper panel). WT and CYLD-/- PMH were pre-incubated with 10 µmol/L YM155 for 4 h. Afterwards PMH were treated for 24 h in combination with TNF-α or Jo2 as indicated (lower panel). DMSO was used as vehicle. Values represent the mean ± SD. aP < 0.05, CYLD-/-vs control group; bP < 0.01, WT vs CYLD-/-; dP < 0.01, WT vs control group; fP < 0.01, CYLD-/-vs control group.
- Citation: Urbanik T, Koehler BC, Wolpert L, Elßner C, Scherr AL, Longerich T, Kautz N, Welte S, Hövelmeyer N, Jäger D, Waisman A, Schulze-Bergkamen H. CYLD deletion triggers nuclear factor-κB-signaling and increases cell death resistance in murine hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(45): 17049-17064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i45/17049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049