Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2014; 20(45): 17049-17064
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049
Published online Dec 7, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049
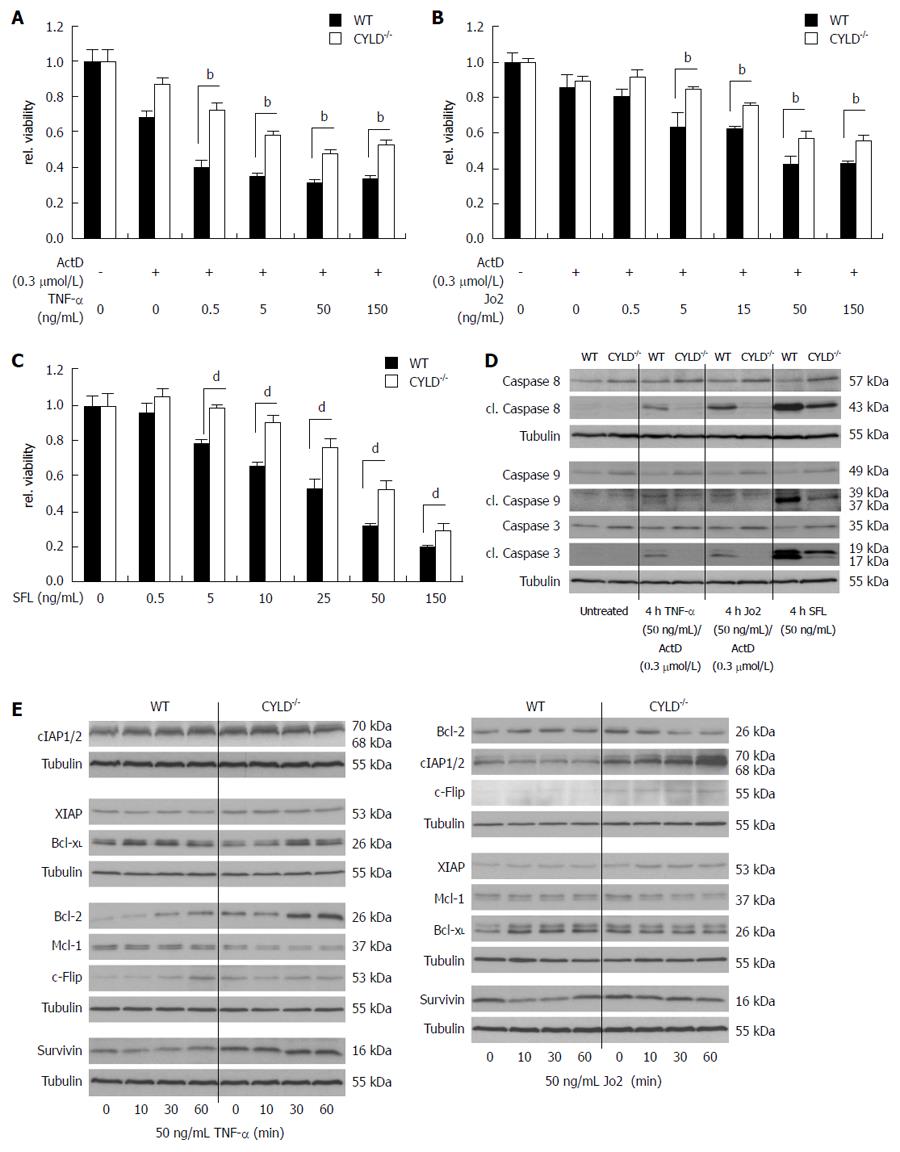
Figure 4 Increased resistance and induction of anti-apoptotic genes in CYLD-/- PMH after death receptor triggering.
A: Freshly isolated PMH were treated for 24 h with increasing concentrations of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and (B) Jo2 in combination with actinomycin D (ActD) as well as with (C) SuperFasLigand (SFL) as indicated; D: Western blot analysis of caspase activation in WT and CYLD-/- PMH after 4 h TNF-α/ActD, Jo2/ActD and SFL treatment with the indicated concentrations; E: Western blot analysis of WT and CYLD-/- PMH for nuclear factor (NF)-κB dependent gene expression after TNF-α (left panel) and Jo2 (right panel) treatment. bP < 0.01, WT vs CYLD-/-; dP < 0.01, WT vs CYLD-/-.
- Citation: Urbanik T, Koehler BC, Wolpert L, Elßner C, Scherr AL, Longerich T, Kautz N, Welte S, Hövelmeyer N, Jäger D, Waisman A, Schulze-Bergkamen H. CYLD deletion triggers nuclear factor-κB-signaling and increases cell death resistance in murine hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(45): 17049-17064
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i45/17049.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i45.17049